Figure 5.
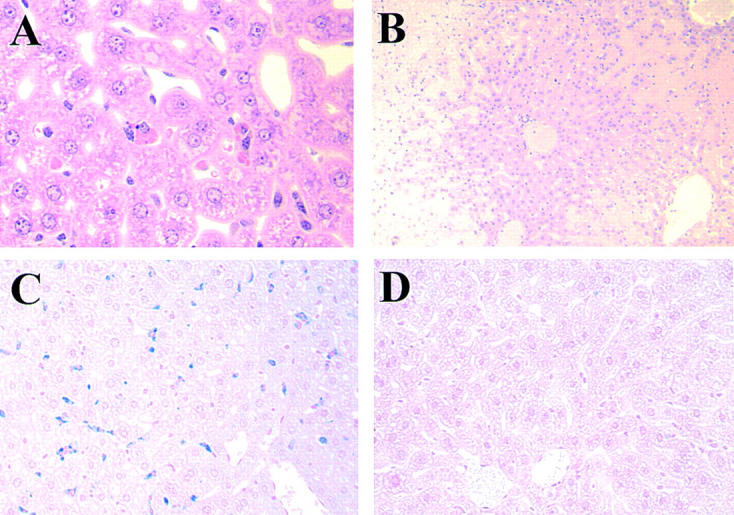
(A) Representative histological appearance of liver 4 d after the injection of 1 mg of the 4C8 IgG2a variant. Note the presence of marked erythrophagocytosis by Kupffer cells (HE; original magnification: ×400). (B) Representative histological appearance of liver from BALB/c mice that died of anemia 2 d after the injection of 250 μg of the 4C8 IgM mAb. Note an enormous accumulation of agglutinated RBCs in sinusoids of liver accompanied by necrosis of hepatic parenchymal cells (HE; original magnification: ×100). (C and D) Representative histological appearance of iron deposits in Kupffer cells from BALB/c and FcRγ-deficient mice after the injection of 1 mg of the 4C8 IgG2a variant. Mice injected with the 4C8 IgG2a variant were killed at day 7. The extent of in vivo RBC destruction by phagocytosis was revealed by coloration of liver sections with Perls iron staining. Note extensive iron deposits in Kupffer cells from BALB/c mice injected with the 4C8 IgG2a mAb (C), in marked contrast to the complete absence of iron deposits in livers from FcRγ-deficient mice injected with the 4C8 IgG2a mAb (D) (original magnification: ×200).
