Figure 5.
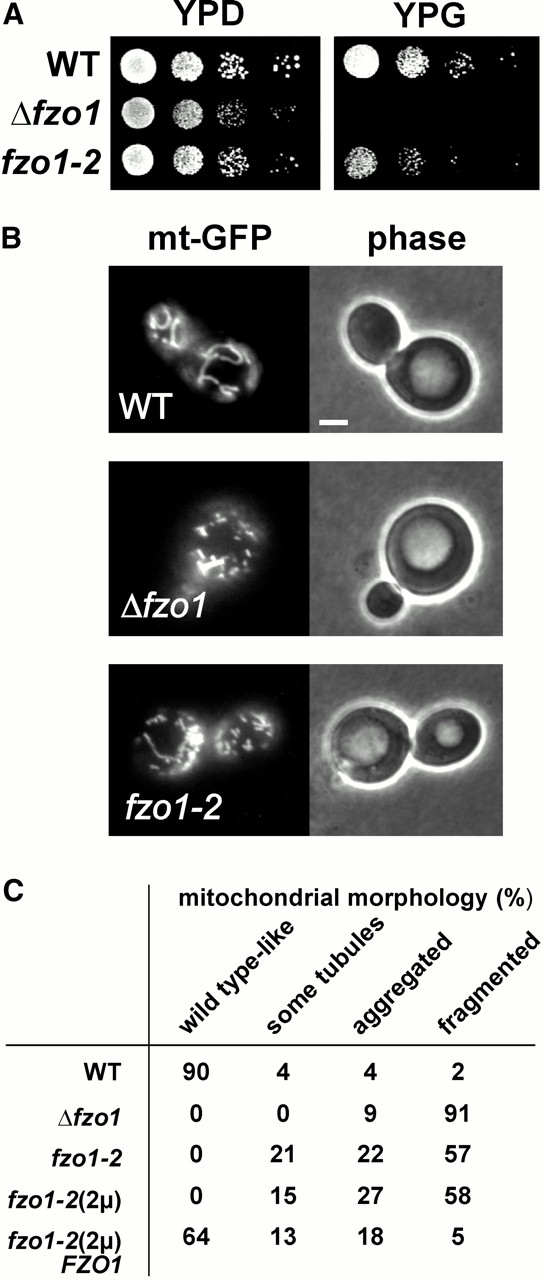
Mutation of the intermembrane space segment compromises the function of Fzo1. (A) Growth phenotype of the fzo1-2 mutant. The fzo1-2 mutant, the Δfzo1 deletion strain, and the isogenic wild type (WT) were grown overnight in liquid minimal medium selective for the maintenance of the plasmid encoding the mutant allele (SD; 2% glucose). Then, 10-fold serial dilutions were spotted onto YPD plates (2% glucose) and YPG plates (3% glycerol). YPD plates were incubated for 3 d at 30°C; YPG plates were incubated for 4 d at 30°C. (B) Mitochondrial morphology of the fzo1-2 mutant. The fzo1-2 mutant, the Δfzo1 strain, and the isogenic wild-type expressing mtGFP were grown overnight in galactose-containing liquid minimal medium (SGal; 2% galactose), selective for maintenance of the plasmid encoding the mutant allele. Living cells were subjected to fluorescence microscopy. Left, the mitochondrial morphology of representative cells is shown; and right, the corresponding phase–contrast images are shown. (C) Quantification of mitochondrial morphology in fzo1 mutants. The following strains were grown to mid-logarithmic growth phase in liquid minimal medium under selection for the plasmids: wild-type (WT; YBW89), Δfzo1 (YBW113), fzo1-2 (YBW117), an Fzo1-2–overexpressing strain (fzo1-2[2μ]; YBW183), and an Fzo1-2–overexpressing strain complemented with a single copy FZO1 wild-type gene (fzo1-2[2μ]FZO1; YBW210). More than 100 cells per culture were examined by fluorescence microscopy and grouped into the following phenotypic classes: wild-type like (mitochondrial reticulum below the cell cortex), some tubules (mostly fragmented mitochondria with a few tubular structures present), aggregated (clustered mitochondrial fragments), and fragmented (evenly distributed mitochondrial fragments). Bar, 2 μm.
