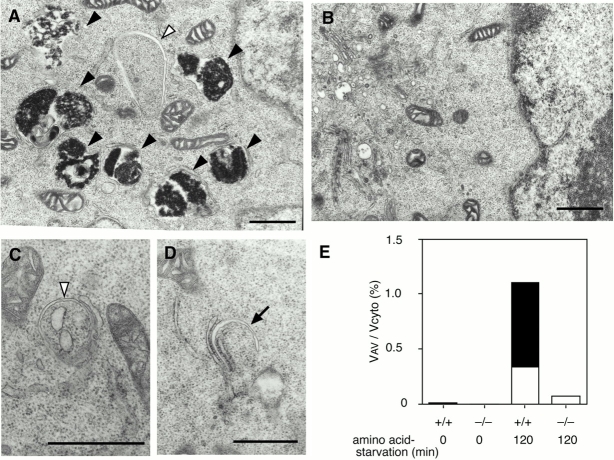
Figure 2.
APG5−/− cells exhibit a block in the autophagic pathway. Wild-type ES cells (A) and APG5−/− cells (B–D) were cultured in Hanks' solution for 2 h, and then fixed and subjected to conventional electron microscopic analysis. The isolation membrane (arrow), autophagosomes or autophagosome-like structures (open arrowheads), and autolysosomes (closed arrowheads) are indicated. (C and D) Rarely detected autophagosome-like structures in APG5−/− cells. As often observed in wild-type cells, isolation membranes develop between cisternae of the ER (C and D). Bars, 1 μm. (E) Morphometric analysis of wild-type (+/+) and APG5−/− (−/−) ES cells before or after amino acid withdrawal. Ratio of total area of autophagosomes (open column) and autolysosomes (closed column) to the total cytoplasmic area is shown.