Figure 4.
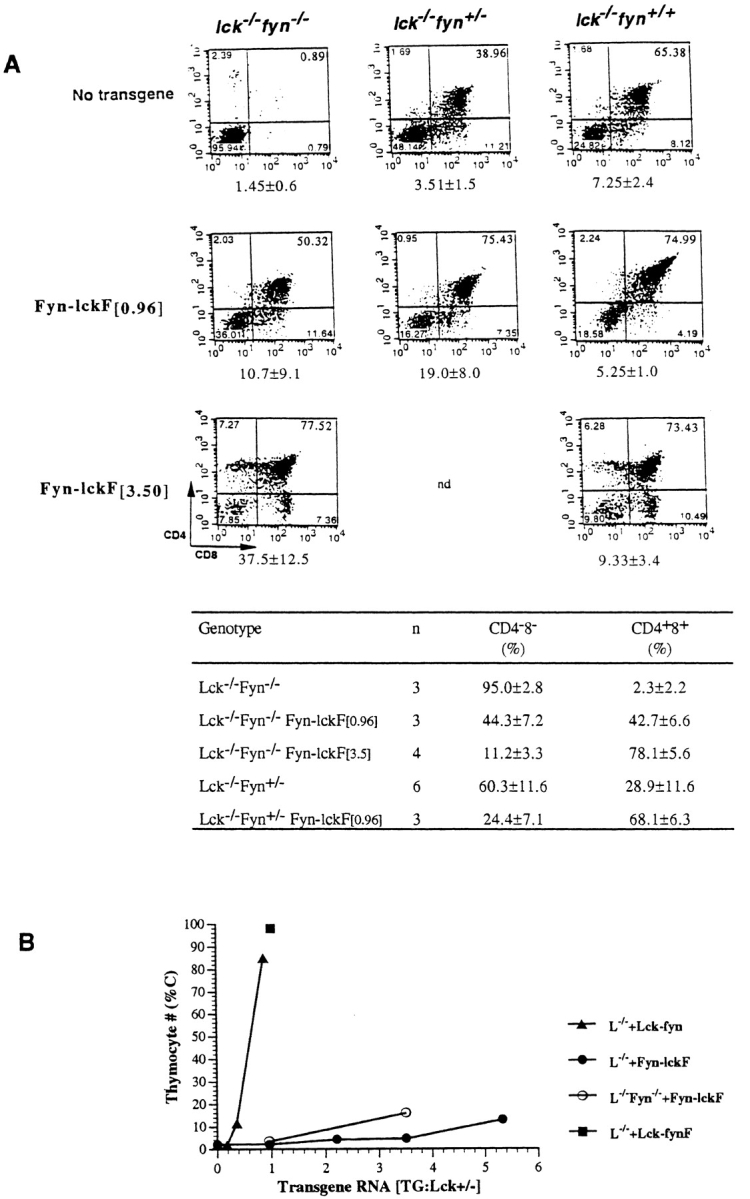
Endogenous Fyn enhances Fyn-lckF function in Lck−/− mice. (A, top) FynT enhances Fyn-lckF–mediated thymocyte differentiation. Thymocytes were recovered from animals of indicated genotypes and were analyzed by flow cytometry. Shown are representative flow cytometric profiles depicting CD4 and CD8 expression determined in three-color immunofluorescence analyses as described in the legends to Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. Numbers of thymocytes recovered from animals in each experimental group are shown beneath the corresponding dual parameter histograms (mean × 10−6 ± SD). (A, bottom) A cumulative analysis of DN and DP proportions in mouse strains as determined by flow cytometry (mean percentage ± SD; n = number of animals of indicated genotypes analyzed). Statistical analyses by two-sample t tests verify that expression of Fyn-lckF is associated with a significant increase in DP thymocytes in both Lck−/−Fyn−/− ([0.96], P = 0.005; [3.5], P = <0.001) and Lck−/−Fyn+/− mice ([0.96], P = <0.001), and that there is a statistically significant impact of Fyn alleles on DP generation in the presence of Fyn-lckF activity (P = 0.009). (B) FynT modulates Fyn-lckF–mediated proliferative expansion. Thymocyte cellularity (C) in reconstituted strains plotted as a function of chimera RNA expression levels. Symbols are mean percentages (adapted from Table ).
