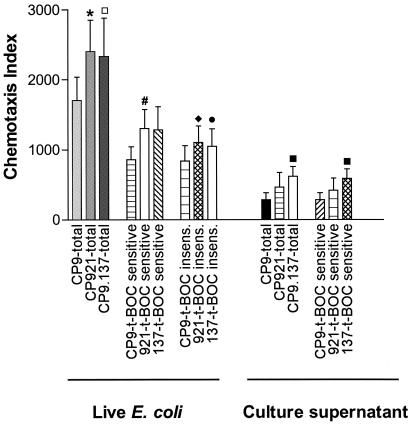
FIG. 4.
In vitro chemotaxis of human neutrophils in response to the live E. coli strains CP9 (wild type), CP921 (O-antigen deficient), and CP9.137 (capsule deficient) and to cell-free culture supernatant from CP9, CP921, and CP9.137. The total deduced N-t-BOC-sensitive and the N-t-BOC-insensitive chemotaxis indices are depicted (see Materials and Methods for details on these indices). The neutrophil response to the positive control (FMLP, 50 nM) was 30,920 ± 2,733 (mean ± SEM), of which 95% ± 1.5% was inhibited by N-t-BOC (500 μM) (n = 14; data not shown in graph). Total chemotaxis was significantly decreased toward the wild-type E. coli strain that possessed an O antigen and capsule (CP9) compared to the isogenic O-antigen-deficient derivatives (CP921) (*, P = 0.002 compared to CP9, paired t test; n = 14 for each strain), and total chemotaxis trended toward being significantly decreased compared to the isogenic capsule-deficient derivative (CP9.137) (□, P = 0.10). Neutrophil chemotaxis toward live E. coli strains was both N-t-BOC sensitive and insensitive. N-t-BOC-sensitive chemotaxis was significantly decreased toward the live, wild-type E. coli strain (CP9) that possessed an O antigen compared to an isogenic O-antigen-deficient derivative (CP921) (#, P = 0.03 compared to CP9, paired t test; n = 14 for each strain). N-t-BOC-insensitive chemotaxis was significantly decreased toward the live, wild-type E. coli strain (CP9) that possessed an O antigen compared to an isogenic O-antigen-deficient derivative (CP921) (⧫, P = 0.008 compared to CP9, paired t test; n = 14 for each strain), and N-t-BOC-insensitive chemotaxis trended toward being significantly decreased compared to the isogenic capsule-deficient derivative (CP9.137) (•, P = 0.052). Neutrophil chemotaxis toward cell-free culture supernatants was primarily N-t-BOC sensitive (100, 97.4, and 96% for CP9, CP921, and CP9.137, respectively); therefore, N-t-BOC-insensitive chemotaxis toward cell-free culture supernatants is not shown. Total and N-t-BOC-sensitive chemotaxis was significantly decreased toward cell-free supernatant from the wild-type stain (CP9) that possessed a capsule compared to an isogenic capsule-deficient derivative (CP9.137) (▪, P = 0.003, paired t test; n = 5 for each supernatant).