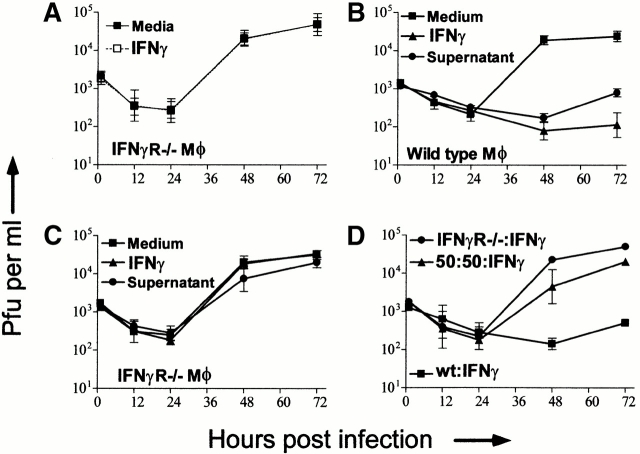
Figure 3.
Secreted mediators from IFN-γ–treated wild-type BMMϕ do not protect IFN-γ unresponsive BMMϕ. (A) BMMϕ from IFN-γR−/− mice and wild-type mice were treated with or without 100 U/ml of IFN-γ, infected at an MOI of 1, and cultured for the indicated times before freeze-thawing and plaque assay (mean ± SEM from three independent experiments). Data is shown for IFN-γR−/− BMMϕ only. IFN-γ efficiently inhibited MCMV growth in wild-type BMMϕ (not shown, see Fig. 1). (B and C) BMMϕ from wild-type (Balb or 129; B) or IFN-γR−/− (C) mice were treated for 48 h with medium, medium plus 100 U/ml IFN-γ, or supernatant from IFN-γ (100 U/ml)–treated wild-type BMMϕ. BMMϕ were then infected at an MOI of 1 and cultured for the indicated times before freeze-thawing and plaque assay (mean ± SEM from three independent experiments). (D) Wild-type (wt; BALB/c or 129), IFN-γR−/− or a 50:50 mix of wild-type and IFN-γR−/− BMMϕ were plated and treated with or without 100 U/ml IFN-γ for 48 h, infected at an MOI of 1 and cultured for the indicated times before freeze-thawing and plaque assay (mean ± SEM from two independent experiments). Results from the IFN-γ–treated cultures are shown. Results from cultures lacking IFN-γ were superimposable to the IFN-γ–treated IFN-γR−/− BMMϕ and are not shown.