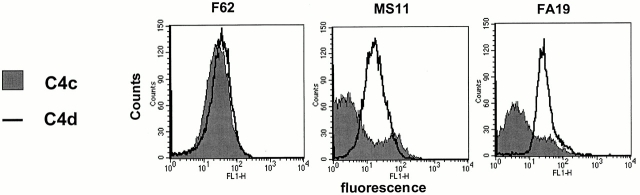
Figure 1.
Demonstration of cofactor activity on gonococcal strains that bind C4bp. Strains F62, MS11, and FA19 were incubated with 20% NHS for 30 min at 37°C, followed by detection of intact C4b fragments remaining on the bacterial surface by flow cytometry. C4bp cofactor activity would result in factor I–mediated cleavage of C4b to C4c and C4d. C4d remains bound to the bacterial surface, whereas the C4c fragment is released into solution. Anti-C4d mAb recognizes both C4b as well as C4d, whereas anti-C4c mAb recognizes only C4b bound to the organism. Therefore, cofactor activity would result in decreased intact C4b detected on the organism (measured with the anti-C4c mAb), with a resultant increase in the C4d/C4c ratio. Consistent with their ability to bind C4bp, both MS11 as well as FA19 show higher C4d/C4c ratios. geo mean flu, geometric mean fluorescence.