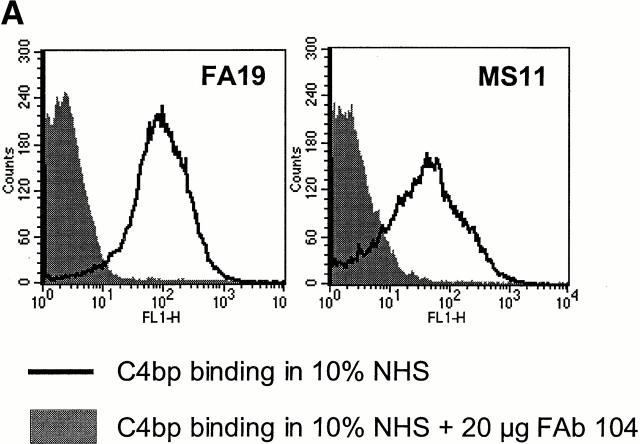
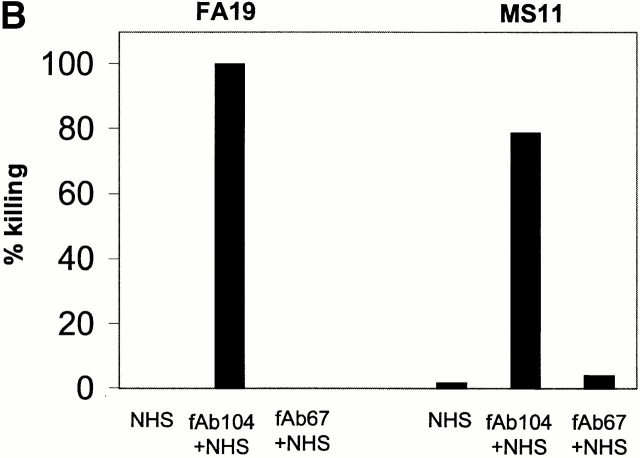
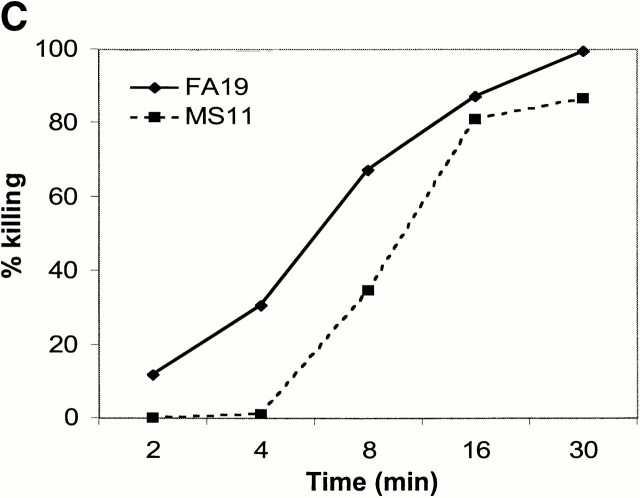
Figure 8.
Functional effects of blocking C4bp binding to gonococci. (A) fAb 104 inhibits C4bp binding to gonococci. 20 μg of fAb fragments generated from mAb 104, when added to 10% NHS, inhibited C4bp binding to FA19 and MS11 equally (gray shaded area). C4bp binding in the presence of NHS alone is shown by the solid line. (B) Diverting C4bp from the bacterial surface converts SR gonococci to an SS phenotype. A serum bactericidal assay was performed to assess the functional effects of inhibiting the binding of C4bp binding to the bacteria. FA19 and MS11 were incubated either with 10% NHS alone, 10% NHS plus 25 μg fAb 104, or 10% NHS plus 25 μg fAb 67 (negative control) for 30 min at 37°C. fAb 104 abrogated C4bp binding to the bacterial surface resulting in 100% killing of FA19 and 80% killing of MS11. NHS alone or NHS with (irrelevant) fAb 67 resulted in no significant killing of either strain. (C) Kinetics of bacterial killing by an unimpeded classical pathway. Abrogation of C4bp binding to the bacterial surface resulted in slow, sustained bacterial killing, with an almost linear decrease in bacterial viability over time of both FA19 (solid line) and MS11 (dotted line).