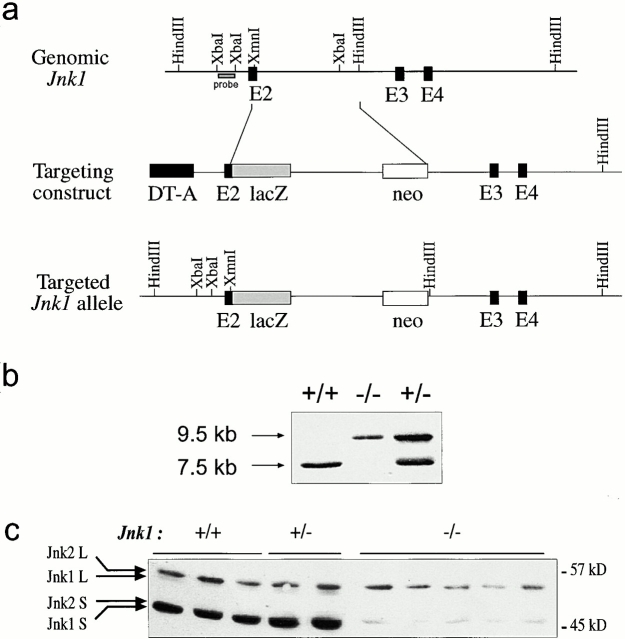
Figure 1.
Targeted mutation of the murine Jnk1 gene in ES cells. (a) The structure of Jnk1 genomic DNA encoding a portion of the JNK1 protein kinase domain (top). The targeting vector (middle) replaced parts of exon 2 with a β-galactosidase gene fused in-frame with exon 2 and a Neor cassette driven by the Rous sarcoma virus promoter. The structure of the targeted allele after homologous recombination is depicted (bottom). DT-A, diphtheria toxin A gene used for negative selection. (b) Genotyping of offspring of mice heterozygous for the targeted Jnk1 mutation. Tail DNA was digested with HindIII and analyzed by Southern blot analysis using the probe indicated in panel a. (c) Western blot analysis of JNK protein expression in primary embryonic fibroblasts. Whole cell extracts (100 μg protein) from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous mutant (−/−) embryonic fibroblasts were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a membrane, and probed with anti-JNK antibodies. The positions of the long (L) and short (S) isoforms of the JNK proteins are indicated.