Figure 5.
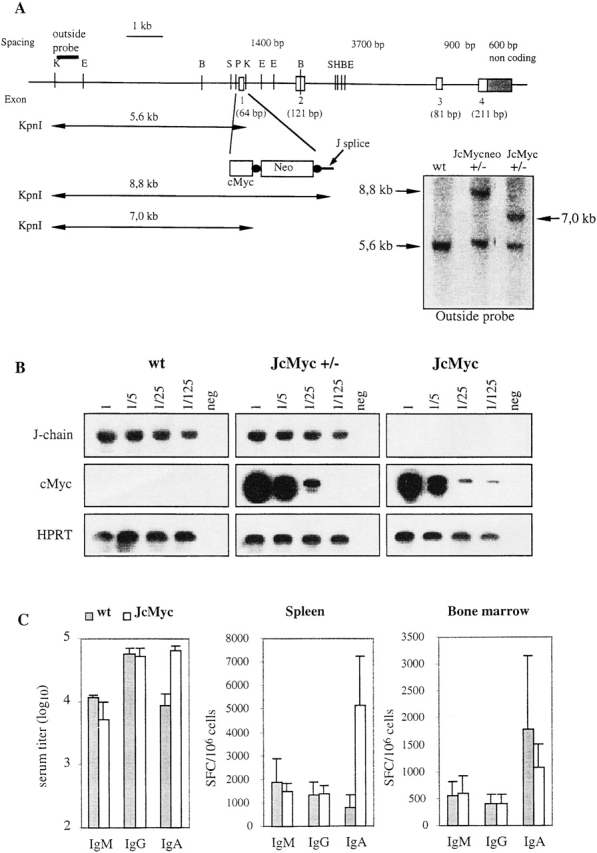
Replacement of the J chain exon 1 with the cMyc gene and Ig production in the resulting JcMyc mice. (A) Disruption of the J chain gene and gene replacement by homologous recombination. Genomic map of J chain locus before and after homologous recombination. Digestion with KpnI gives an endogenous band of 5.6 kb while the recombined locus gives a band of 8.8 kb for JcMycneo and 7.0 kb for JcMyc after removal of the neor gene. Southern blot analysis of the recombined J chain locus showing wt, heterozygous (+/−) JcMycneo, and heterozygous (+/−) JcMyc using an outside probe (not present in the construct used for targeting). E, EcoRI; B, BamHI; S, SacI; P, PstI; K, KpnI; and H, HindIII. (B) Expression analysis by RT-PCR for J chain and cMyc transcripts in wt, JcMyc heterozygous (JcMyc+/−), and JcMyc mice. Primers for J chain were located in exon 1 and in exon 4 of the J chain locus. Primers for cMyc transcripts were located in the 3′ end of the cMyc gene and in the exon 4 of the J chain locus. Shown is also analysis for HPRT transcripts as a cDNA control. (C) Serum IgM, IgG, and IgA levels in wt and JcMyc mice at the age of 4 mo (n = 3) and number of Ig-secreting cells per 106 cells from wt and JcMyc spleen and bone marrow as detected by ELISPOT assay (n = 3). Data shown from one out of two experiments giving similar results. SFC, spot forming cell.
