Figure 3.
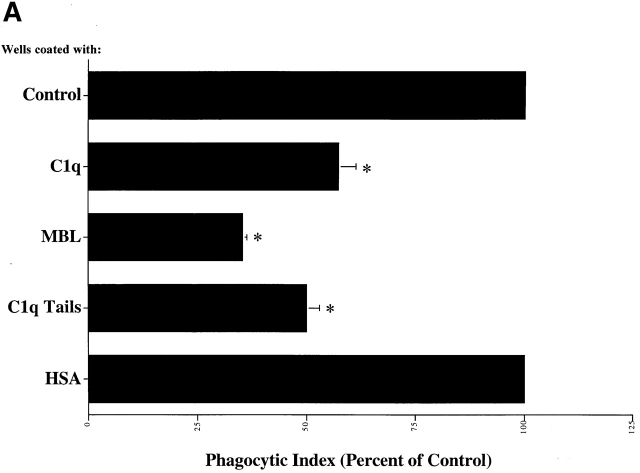
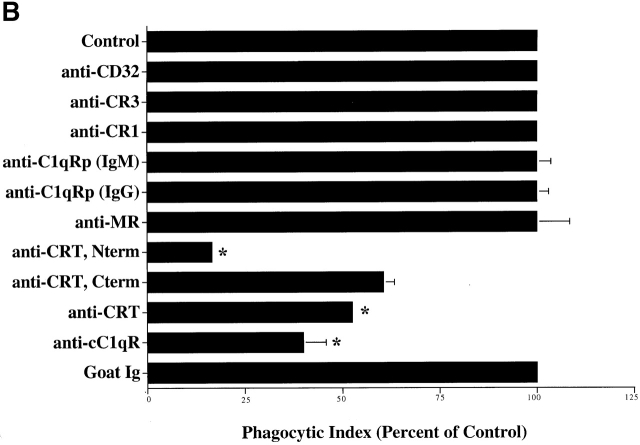
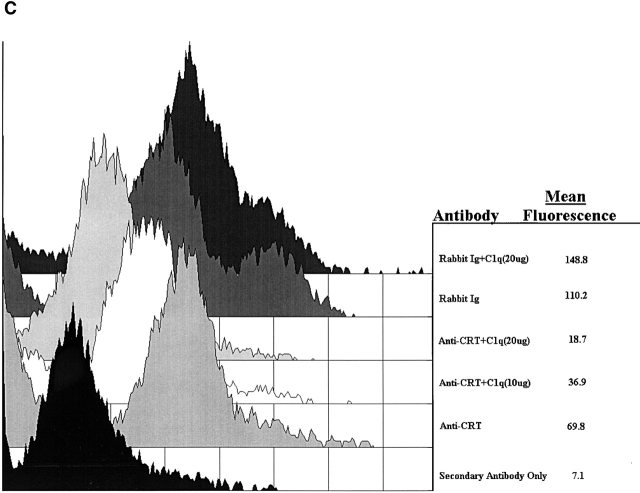
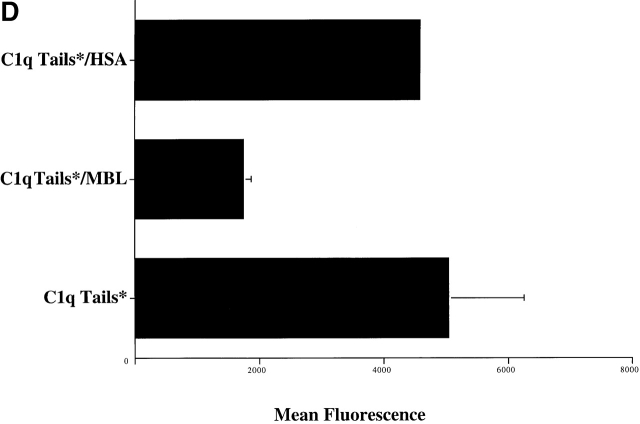
C1q and MBL facilitate clearance of apoptotic cells via cell-surface CRT. (A) Modulation of membrane receptor(s) by surface-bound C1q, C1q tails, or MBL. Macrophages were plated onto wells coated with control protein (HSA), MBL, C1q, or C1q tails. Apoptotic cells were then added for a phagocytosis assay. n = 7 ± SEM (control mean phagocytic index = 38.5 ± 4.4, P < 0.01). (B) Anti-CRT antibodies inhibit uptake of apoptotic cells by HMDMs. Other anti-receptor antibodies had no effect. anti-Nterm, anti-CRT, NH2 terminus; anti-Cterm, anti-CRT, COOH terminus; anti-MR, anti-mannose receptor; anti-CR3, anti-complement receptor 3; anti-CR1, anti-complement receptor 1. n = 4 ± SEM (control mean phagocytic index = 40.0 ± 4.3, P < 0.05). (C) Binding of anti-CRT antibody to the surface of HMDMs. Several polyclonal anti–human CRT antibodies were found to bind to the surface of HMDMs (see Materials and Methods) in a similar fashion. Binding of a rabbit anti–human polyclonal anti-CRT antibody was blocked by C1q. C1q did not inhibit binding of irrelevant antibody HMDM surfaces (inset). n = 3, representative experiment shown. (D) MBL and C1q bind to same receptor. C1q tails were FITC-conjugated (see Materials and Methods) and bound to HMDM surfaces. Unlabeled, whole MBL decreased this binding when incubated with the HMDMs along with the FITC-labeled tails, n = 3.