Figure 3.
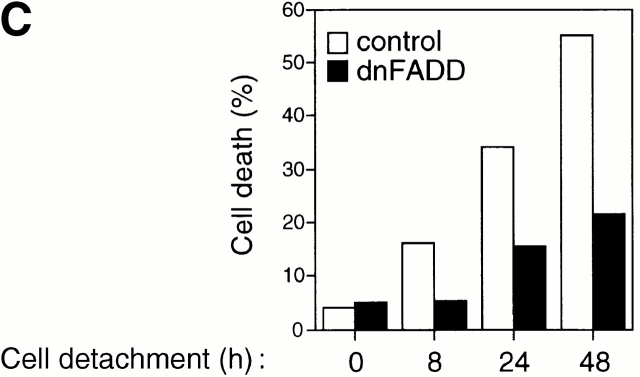
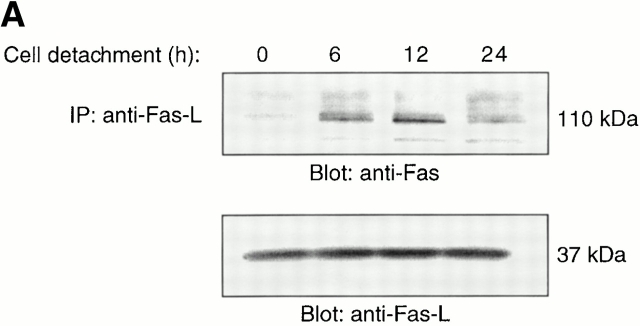
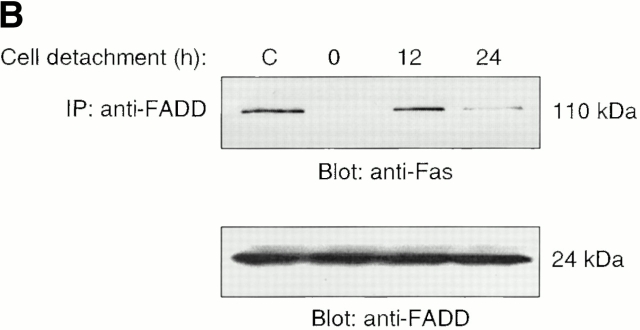
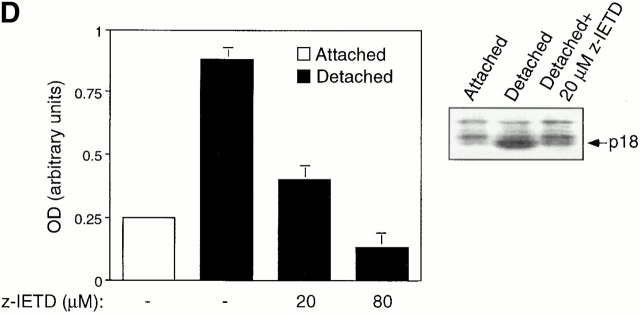
Cell detachment induces Fas/Fas-L interaction, DISC formation, and caspase-8 activation in HUVECs. Inhibition of anoikis by dnFADD and caspase-8 inhibitors. (A) Cell lysates were prepared from adherent HUVECs and from HUVECs that had been kept in suspension for the indicated times, and the lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation analysis by anti–Fas-L antibodies (clone 33). Immunoprecipitates (IP) were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Fas antibodies (clone 13; top). The membranes were stripped and reprobed with anti–Fas-L antibodies (clone 33) to confirm equal amounts of Fas-L in the precipitates (bottom). Similar results were obtained when anti–Fas-L antibody G247-4 was used (data not shown). (B) The cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitations by anti-FADD antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Fas antibodies (clone 13; top), and the membranes were stripped and reprobed with anti-FADD antibodies to confirm equal amounts of FADD in the precipitates (bottom). C, Control cell lysate prepared from Jurkat T cells that had been activated by T cell receptor stimulation. (C) HUVECs were transiently transfected with an empty vector (control) or with an expression plasmid encoding dnFADD, together with plasmid coding for the green fluorescent protein (GFP). 24 h after transfection, the cells were either kept adherent or kept in suspension for the indicated time periods. The cells were then washed and propidium iodide was added for 20 min on ice. Apoptosis analysis by FACS® was carried out in the double positive cell population for propidium iodide and fluorescent GFP. In a separate experiment, we monitored apoptosis by staining the cells with Hoechst dye and found that results obtained with propidium iodide and Hoechst were indistinguishable from each other (not shown). Thus, the results obtained with the Hoechst dye confirm that cell death observed under our experimental conditions results from apoptosis, rather than necrosis. (D) HUVECs were left adherent or kept in suspension for 12 h in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of caspase-8 inhibitor z-IETD-fmk. In the left panel, apoptosis was determined by DNA fragmentation analysis; bars indicate SD in a representative experiment done in triplicate. In the right panel, cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti–caspase-8 antibody (Ab-1) that detects the p18 active form of the enzyme.