Figure 8.
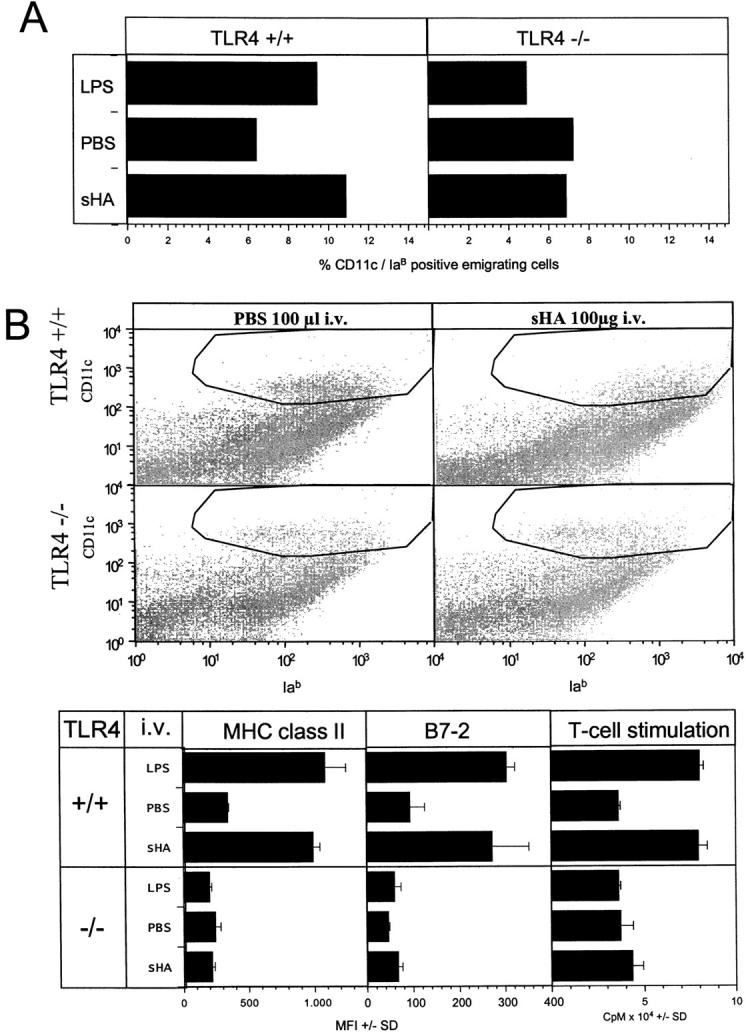
In vivo relevance of the sHA-induced DC stimulation. (A) Full thickness skin was obtained from the outer epidermal sheet of the ears of C57BL/10ScSn wild-type (TLR+/+) and TLR-4−/− C57BL/10Cr mice at three animals per group. Ear sheets were floated on supplemented RPMI 1640 with or without addition of 30 μg/ml sHA or 100 ng/ml LPS. After 24 h, cells that had migrated into the culture medium were collected and double stained for CD11c and IaB expression. Large, highly CD11c and IaB-positive cells were considered as DCs and the percentage was calculated by flow cytometry. A representative of two independent experiments is shown. (B) 100 μg/animal sHA or 100 μl PBS was injected intravenous into the tail vein of C57BL/10ScSn wild-type (TLR+/+) and TLR-4 −/− C57BL/10Cr mice at three animals per group. The mice were killed after 12 h and large, highly CD11c-positive cells in the spleens were analyzed for their IaB and B7–2 expression by flow cytometry. Results are shown as mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) in the marked gates ± SD. Further, DCs were isolated from spleen cells and 5 × 103 DCs were restimulated for 4 d with 105 allogenic T cells from BALB/c mice. T cell proliferation was determined on day 4 by addition of 1 μCi of 3[H]thymidine for the final 18 h. Results are shown as counts per minute (CPM) ± SD of triplicate wells. A representative of two independent experiments is shown.
