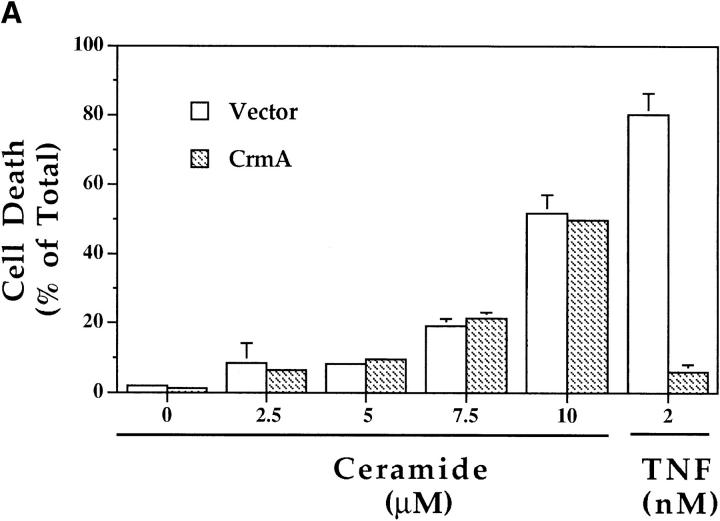
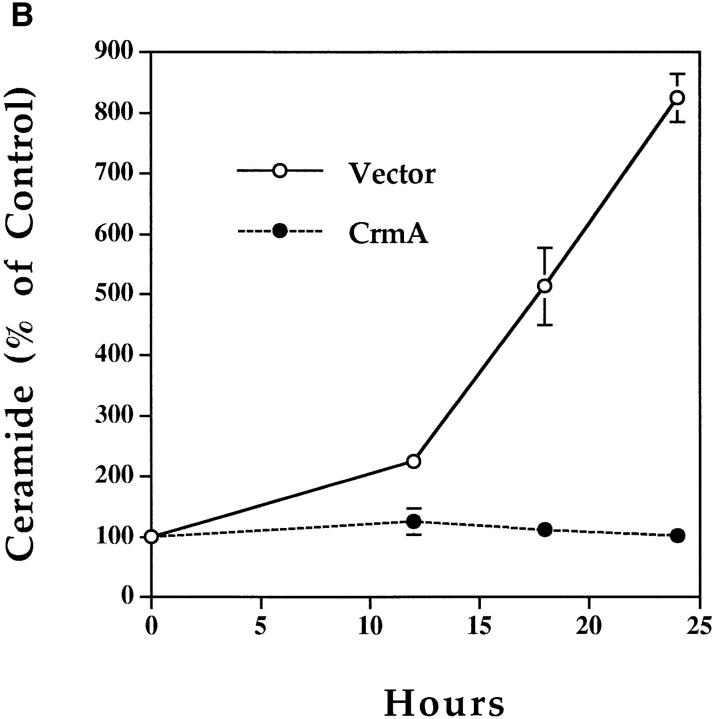
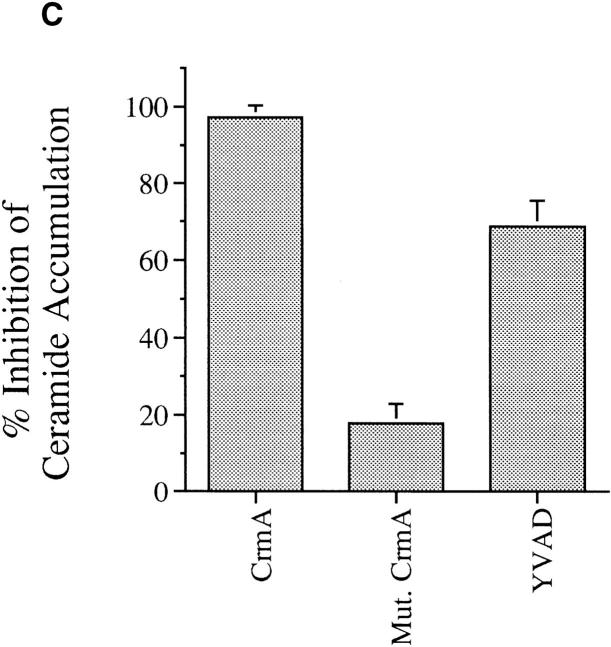
Figure 3.
Effects of CrmA on the TNF-α–activated ceramide pathway. (A) CrmA protects from TNF-α–induced, but not ceramide-induced, cell death. TNF-α–sensitive MCF-7 cells transfected with either pcDNA3 vector (open bars) or pcDNA3/crmA (filled bars) were seeded in 24-well plates at 5 × 104 cells/well in 2% FBS, rested overnight, and then treated with the indicated concentrations of C6-ceramide or 2 nM TNF-α. Cell death, determined by the inability to exclude trypan blue, was evaluated at 48 h. (B) CrmA inhibits ceramide generation after TNF-α stimulation. The CrmA-expressing MCF-7 cells (filled circles) and their vector control cells (open circles) were treated with TNF-α as in Fig. 1. Ceramide levels were measured at the indicated time points as in Fig. 1. Results are the average of three experiments with the standard deviation indicated. (C) Antiproteolytic activity of CrmA is important in inhibiting ceramide accumulation. Cells expressing CrmA, point-mutant CrmA, or wild-type MCF-7 cells pretreated 1 h with 50 μm Ac-YVAD-CHO (Bachem, King of Prussia, PA) were treated, along with their respective controls, with 1.2 nM TNF-α for 18 h. Ceramide was then measured as in Fig. 1. Percent inhibition was calculated by comparison with the results from TNF-α– treated controls. The average of three experiments is shown.