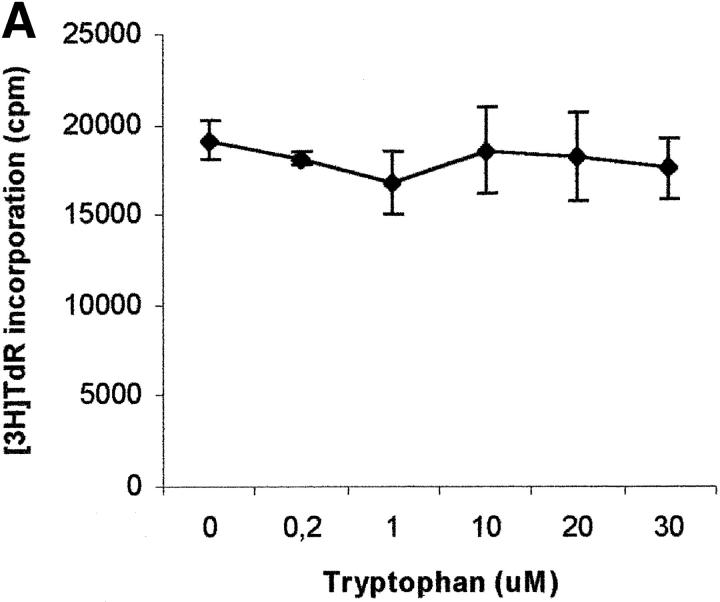
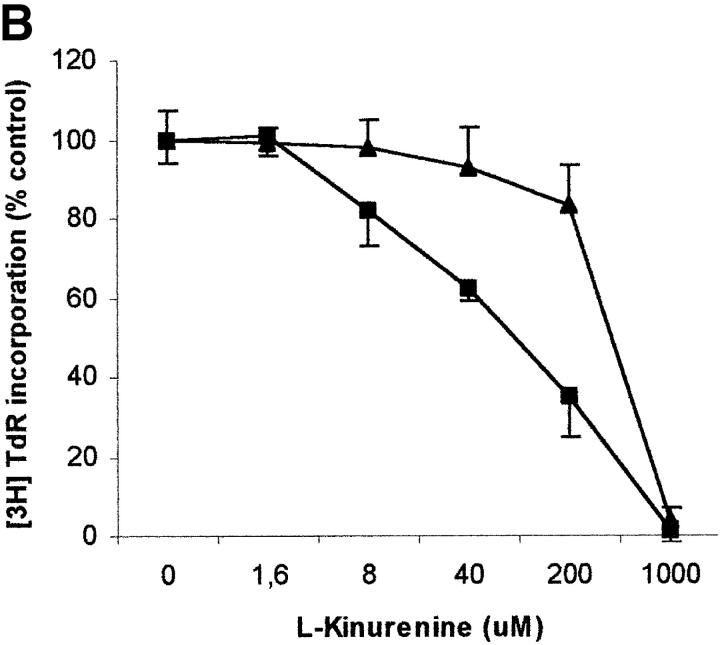
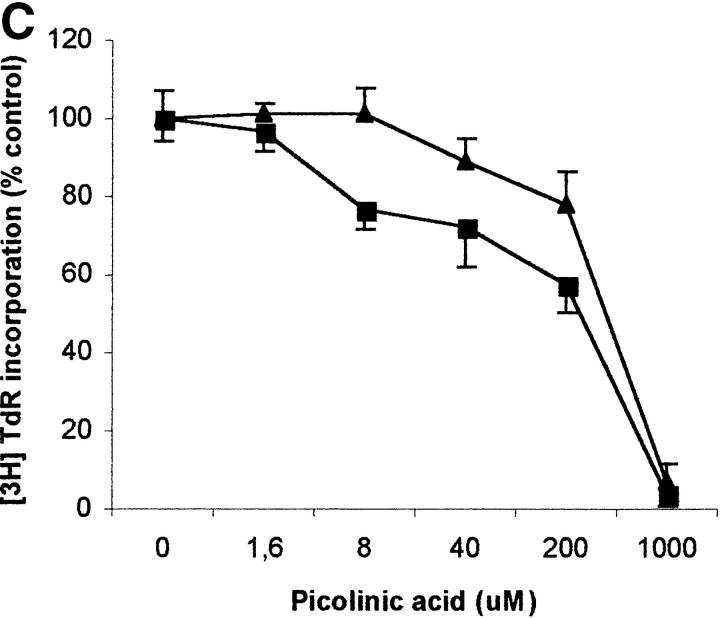
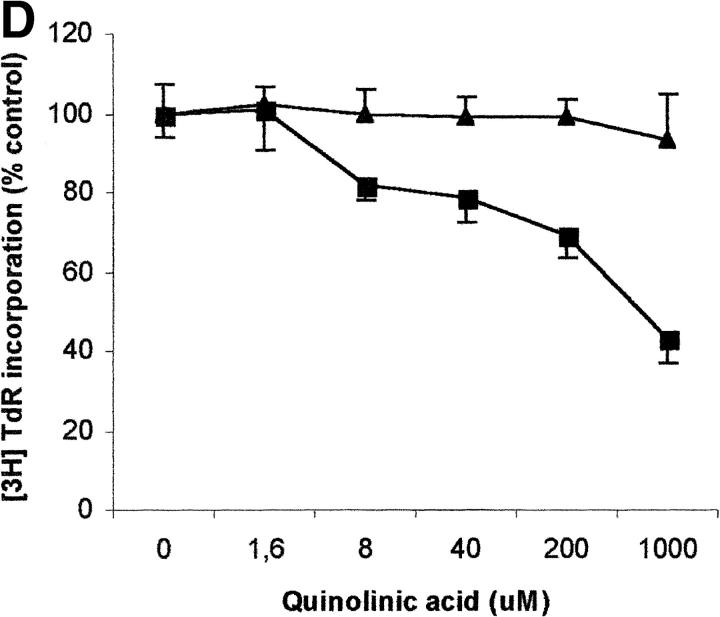
Figure 6.
Effect of tryptophan concentration on tryptophan catabolites-dependent inhibition of T cell proliferation. (A) Increasing concentrations of l-tryptophan were added to PBLs activated and cultured in a medium devoid of tryptophan. Cell culture was stopped after 96 h from PHA activation, and proliferation was evaluated by measuring 3[H]thymidine incorporation. (B–D) Increasing concentrations of l-kynurenine (B), picolinic acid (C), and quinolinic acid (D) were added to PBLs activated and cultured in tryptophan-free medium (▪——▪), or in the tryptophan-free medium supplemented with 26 μM l-tryptophan (▴——▴). Controls were represented by untreated PHA-activated PBLs grown in tryptophan-free medium and in the same medium supplemented with l-tryptophan, respectively. Cell culture was stopped after 96 h from PHA activation, and proliferation was evaluated by measuring 3[H]thymidine incorporation. To permit comparison, proliferation has been normalized to the control cultures (PHA-activated PBLs grown in tryptophan-free medium: 19,134 ± 1,109 cpm; PHA-activated PBLs grown in tryptophan-free medium supplemented with l-tryptophan: 20,021 ± 1,776 cpm). m ± 1 SD, n = 3.