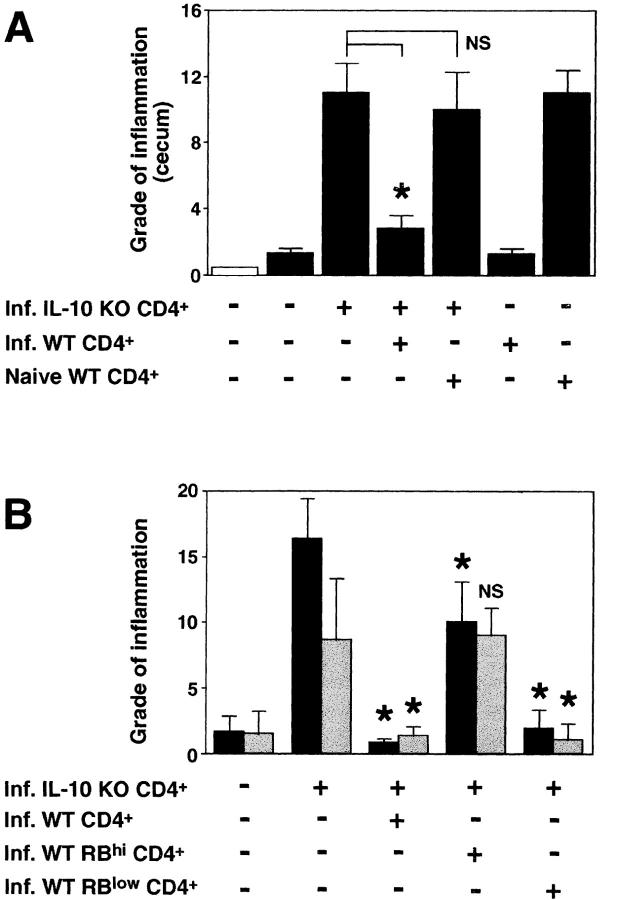
Figure 2.
CD45RBlow CD4+ cells from H. hepaticus–infected WT mice protect RAG KO animals from colitis induced by IL-10 KO CD4+ cells plus bacterial infection. (A) H. hepaticus–infected RAG KO mice (solid bars) were inoculated with CD4+ cells from infected IL-10 KO mice and CD4+ cells from naive or infected WT mice as indicated (4 × 105 of each population). Intestinal pathology was analyzed 4 wk later. Naive (open bar) and infected RAG KO animals receiving no cells were included as controls. Bars represent mean histology scores ± SD of three mice per group except for groups receiving WT cells alone, in which case, due to limited cell numbers, only two mice per group were used. Similar results were seen in ascending colon (although histology scores were lower) and when disease was induced by the transfer of CD4+ cells from naive IL-10 KO mice (not depicted). (B) Infected RAG KO mice were given either no cells or CD4+ cells from infected IL-10 KO mice and CD4+, CD45RBhi CD4+, or CD45RBlow CD4+ cells from infected WT mice as indicated (4 × 105 of each population). Pathology in the cecum (solid bars) and ascending colon (gray bars) were analyzed 4 wk later. Bars represent mean histology scores ± SD of six or seven mice per group pooled from two separate experiments except for the group receiving IL-10 KO CD4+ cells plus infected WT CD4+ cells (n = 3), which was included in only one of the experiments. Statistical significance was tested for groups receiving IL-10 KO cells. *, P < 0.05 compared with mice receiving IL-10 KO cells alone.