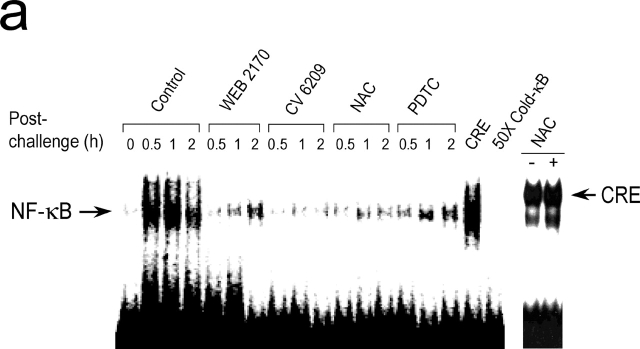
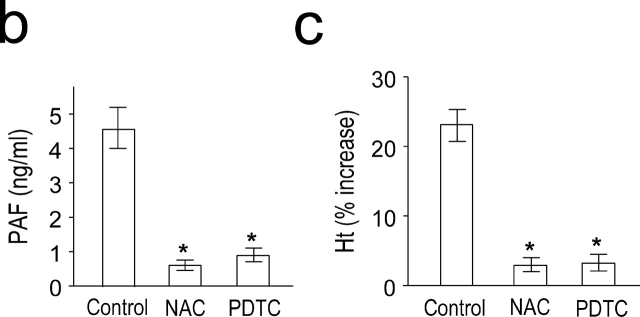
Figure 2.
PAF-induced activation of NF-κB during anaphylaxis and its association with the development of the late phase of anaphylaxis. (a) NF-κB activation during anaphylaxis and its inhibition by the pretreatment with PAF antagonists and NF-κB inhibitors. After the challenge, lungs were removed at the indicated time points and the time course of NF-κB activation was measured by gel shift assay with nuclear extracts (n = 3–5 for each time point). For gel shift assay of CRE mobilization, lungs were removed 1 h after challenge. A representative of four independent experiments is shown. (b and c) Inhibition of the second phase of increase in plasma PAF (b) and hematocrit value (c) by NF-κB inhibitors. Blood was collected 7.5 h after the challenge. Results for all panels are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three to seven separate experiments (n = 4 for each time point). *, P < 0.01 versus control; Mann-Whitney U test.