Figure 2.
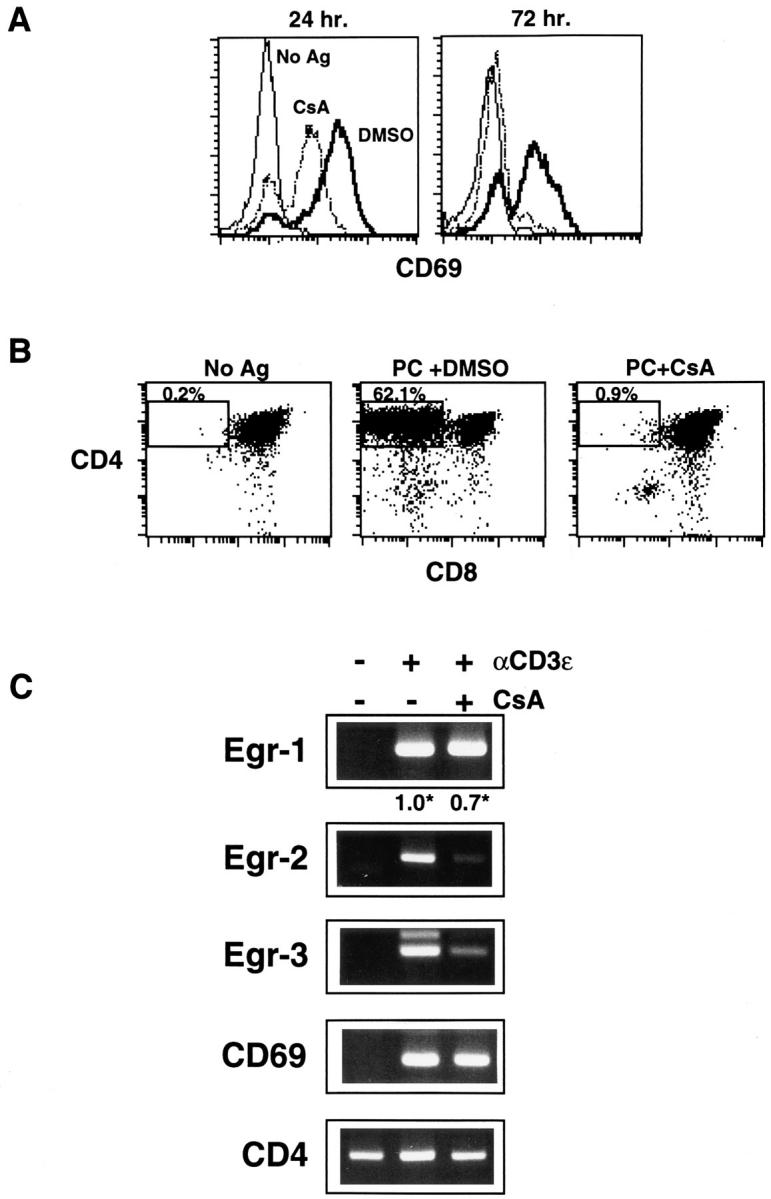
DPK cell differentiation and Egr-2,3 mRNA induction is cyclosporin A sensitive, while Egr-1 mRNA induction is cyclosporin A resistant. (A, B) DPK cells were cultured with DCEK-ICAM fibroblast antigen presenting cells and 2 μM pigeon cytochrome c peptide in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml cyclosporin A, or appropriate dilution of solvent (DMSO) as indicated. Cells were harvested and stained for CD69 after 1 or 3 d in culture (A) or stained for CD4 and CD8 after 3 d in culture (B). (C) RT-PCR analysis of total RNA derived from DPK cells activated for 6 h with immobilized anti-CD3ε mAb in the presence or absence of 300 ng/ml cyclosporin A, using Egr-1, Egr-2 (Krox-20), CD4, CD69 or Egr-3 primers. (*) Also shown for the indicated samples is the relative level of Egr-1 cDNA normalized to expression of CD4 cDNA as determined by competitive RT-PCR assay. The identity of the lower major band in Egr-3 RT-PCR was verified by sequencing.
