Figure 4.
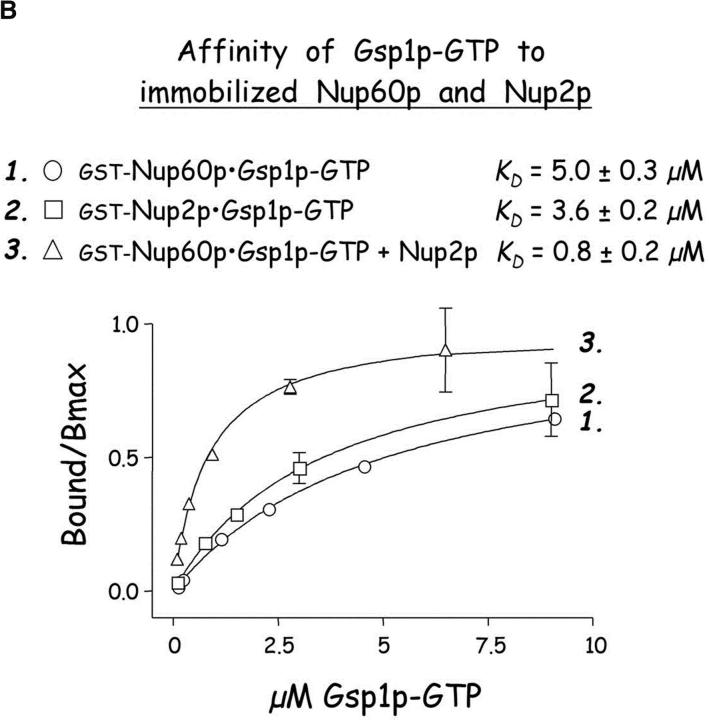
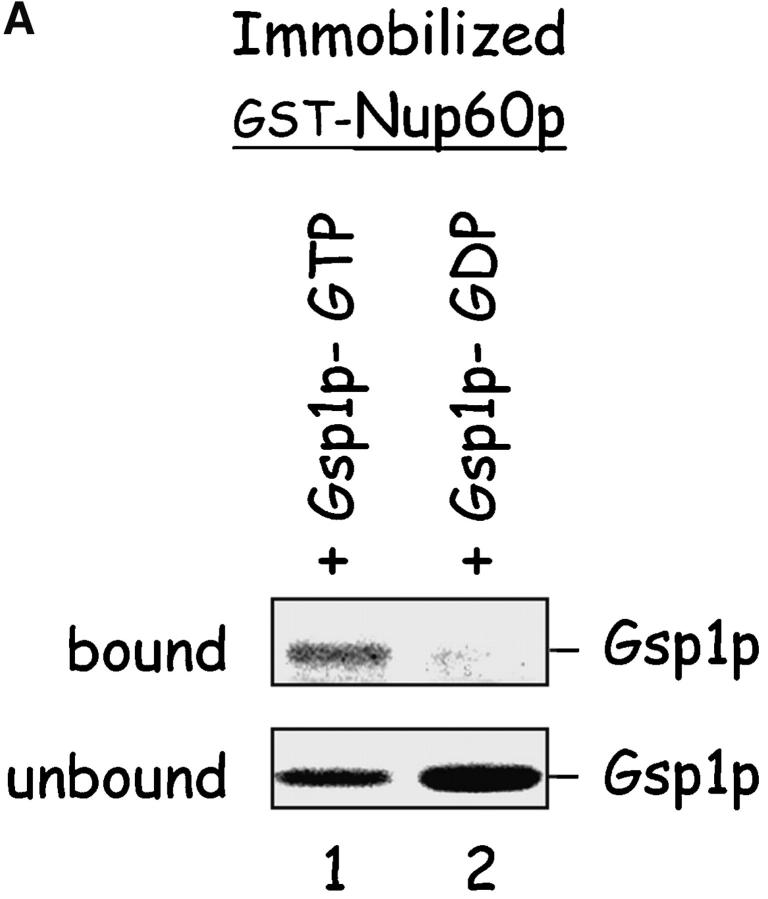
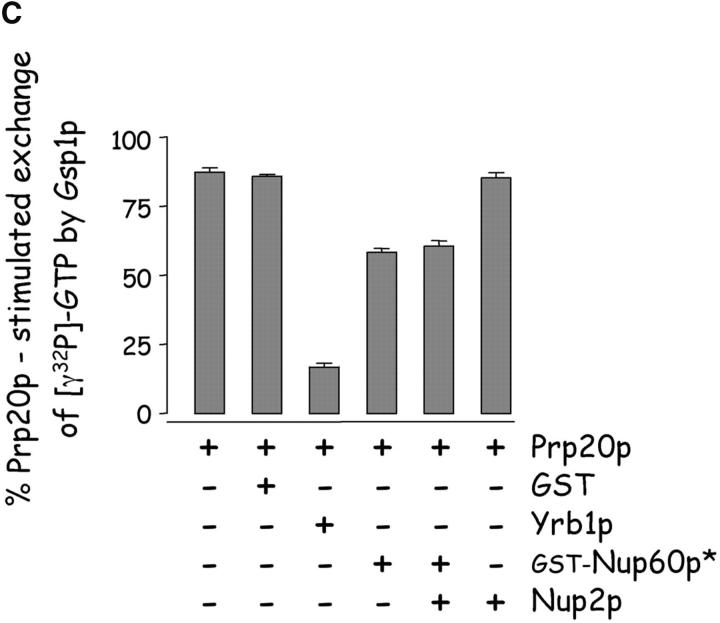
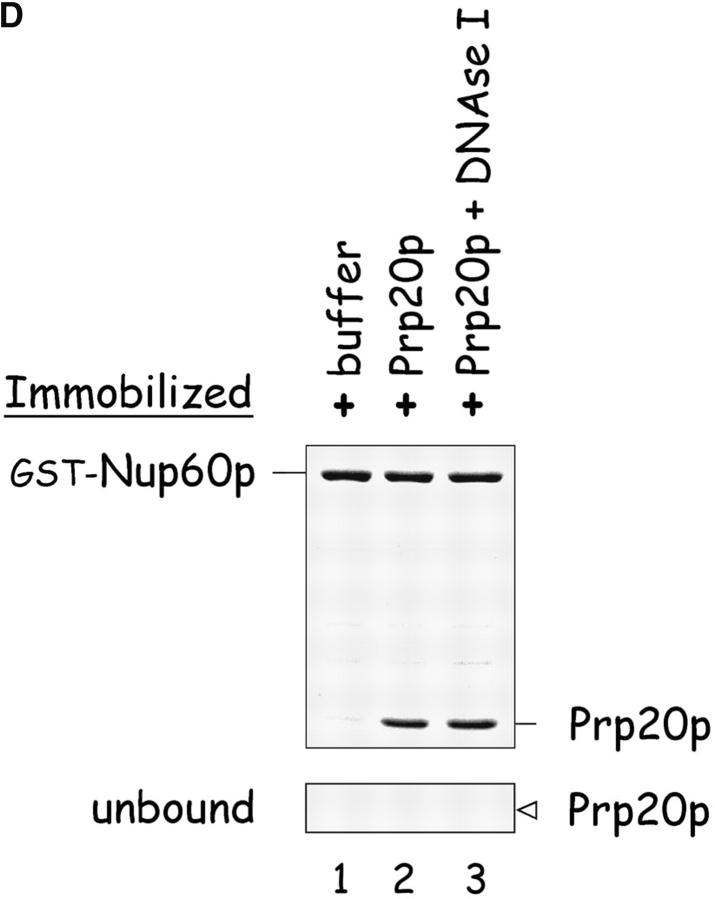
Nup60p binds Gsp1p–GTP and Prp20p, and functions as a Gsp1p GDI. (A) Nup60p binds Gsp1p–GTP. GST-Nup60p (1 μg) was immobilized on beads and incubated with His-Gsp1p (2 μg) preloaded with GTP or GDP. After 1 h at 4°C, bound and unbound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized with Coomassie blue. Note that Nup60p binds Gsp1p–GTP, but not Gsp1p–GDP. (B) Affinity of Gsp1p–GTP to Nup60p, Nup2p, and Nup60p–Nup2p complexes. GST–Nup-coated beads were incubated with various concentrations of His-Gsp1p–[γ-32P]GTP for 2 h at 4°C in binding buffer with 10 mg/ml BSA and protease inhibitors. The concentrations of GST–Nup60p and GST–Nup2p within beads were 800 nM and 1.5 μM, respectively. The dissociation constants (KD) of the Nup2p–Gsp1p–GTP complex and the Nup60p–Gsp1p–GTP complex in the presence and absence of 500 nM Nup2p were calculated as described in Materials and methods. Results were plotted as a fraction of maximal Gsp1p–GTP bound versus Gsp1p–GTP concentration. Each data point was performed in duplicate and the error bars represent SEM. Note that Nup60p and Nup2p cooperate to bind Gsp1p–GTP. (C) Nup60p inhibits the Prp20p-stimulated release of GTP from Gsp1p. His-Gsp1p–[γ-32P]GTP immobilized on nickel-coated agarose beads (15 nM Gsp1p–GTP within the beads) was incubated with 0.9 nM Prp20p and 1 mM GDP, plus 4 μM GST–Nup60p (aa 188–539), Yrb1p, Nup2p, Kap95p, or GST. GST–Nup60p (aa 188–539) (indicated by asterisk) was used instead of full-length Nup60p due to its superior solubility and protease resistance. After 10 min, Prp20p activity was stopped with ice-cold buffer, beads were washed, and the [γ-32P]GTP that remained bound to the beads was quantified by scintillation counting. Each data point was performed in duplicate and error bars represent SEM. Note that Nup60p reduces (but does not abolish) the activity of Prp20p. (D) Nup60p binds Prp20p. GST–Nup60p (1 μg) was immobilized on beads and incubated with purified Prp20p (1 μg) in the presence or absence of DNAse I and RNAse I (1 U and 1 μg, respectively). After 1 h at 4°C, unbound and bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized with Coomassie blue staining. Note that purified Prp20p binds Nup60p.