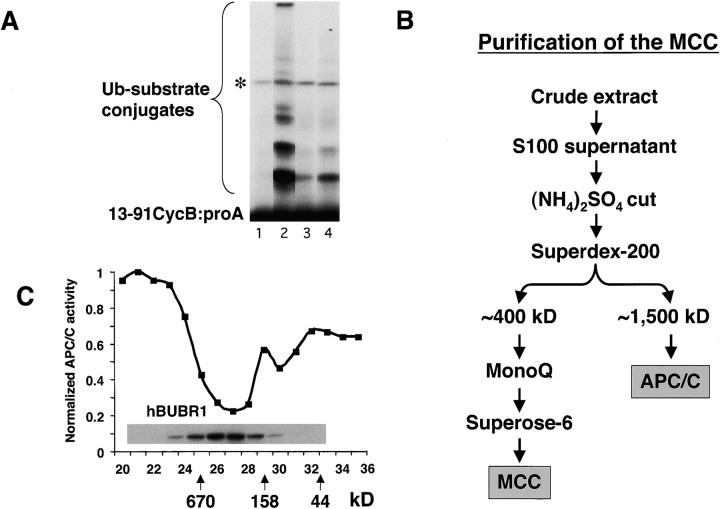
Figure 1.
Identification of an APC/C inhibitor that copurifies with hBUBR1 kinase. (A) Identification of APC/C inhibitory activity in mitotic lysates. Mitotic lysate (S100) was fractionated through a Superose 6 gel filtration column by FPLC and proteins eluting at approximately the 300–400-kD range were found to inhibit APC/C activity. To maintain some physiological relevance to the APC/C inhibition assays, equal cell equivalents of APC/C and the various column fractions were used. Purified mitotic APC/C was incubated for 30 min with either buffer B alone (lane 2) or fractions from the 300–400-kD range of the Superose 6 column (lane 4) and then assayed for ubiquitin ligase activity. The same column fractions were assayed without addition of APC/C to monitor contaminating APC/C activity (lane 3). A reaction containing only substrate served as a negative control (lane 1). Asterisk denotes an iodinated contaminant bacterial protein that is not a substrate for APC/C and was excluded from the quantitation. (B) Flow chart of the purification of the APC/C inhibitory complex from HeLa cells. (C) Inhibitor of APC/C cofractionates with the hBUBR1 kinase complex. The elution profiles of hBUBR1 (inset) and APC/C inhibitory activity from the final Superose 6 column is shown. Arrows point to thyroglobulin (670 kD), γ-globulin (158 kD), and ovalbumin (44 kD), which served as migration standards.