Figure 4.
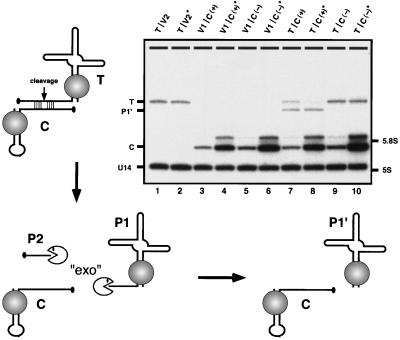
Cleavage in trans. The in vivo cleavage efficiency in trans was assessed with snorbozyme genes that encode the catalytic and target elements in separate transcripts. The catalytic portion of the ribozyme (46 nt) was embedded in the mini-U3 variant (U3del) in place of nucleotides 6–60; C(+) refers to the active ribozyme, and C(−) refers to the defective ribozyme. The target sequence (19 nt) was placed into U3*, replacing the same wild-type segment; the target RNA is designated T. U3 snoRNA derivatives containing substrate and catalytic sequences were coexpressed in yeast cells from two different low-copy plasmid vectors (V1 and V2). To determine whether the ribozyme level was limiting, the catalytic RNA was also expressed from a multicopy vector (V*). The diagram depicts the principal events predicted to occur, and the Northern blot identifies the RNA species observed. Bands marked on the Northern blot correspond to: target RNA (T), cleaved and trimmed byproduct (P1′), catalytic RNA (C), U14 snoRNA (≈130 nt) as a control for RNA loading, and the positions of 5.8S (≈160 nt) and 5S (≈120 nt) rRNAs. Samples are given two-part names, which refer to the vector pairs carrying the target and catalytic RNA genes, respectively. Combinations of empty vectors and experimental genes are also included as controls. The samples are arranged as follows: lanes 1 and 2, target molecule (T) only, produced in the presence of low- and high-copy empty vectors (V2 and V2*); lanes 3 and 4, active catalytic RNAs produced from low- and high-copy vectors, C(+) and C(+)*, respectively, in the presence of empty vector V1; lanes 5 and 6, inactive catalytic RNA produced from low- and high-copy vectors, C(−) and C(−)*, respectively, in the presence of empty vector V1; lanes 7 and 8, target molecules coexpressed with active catalytic RNA encoded by low- and high-copy vectors, C(+) and C(+)*, respectively; lanes 9 and 10, target molecules coexpressed with inactive catalytic RNA encoded by low- and high-copy vectors, C(−) and C(−)*, respectively. The minor bands observed just above the catalytic RNAs (C) correspond to molecules with extensions at the 3′ end (22). The cleavage efficiency for active ribozyme produced from low- and high-copy vectors is estimated at ≈60% and 90%, respectively (lanes 7 and 8; compare with lanes 9 and 10).