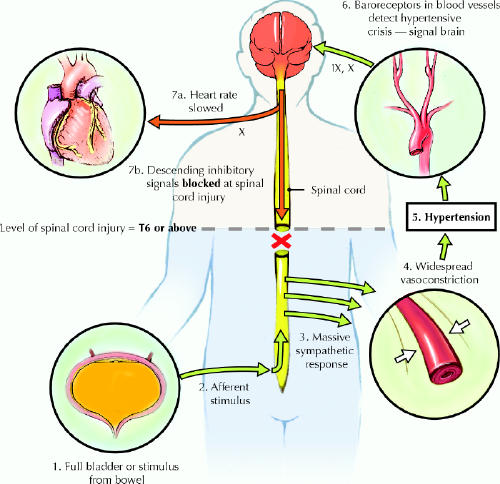
Fig 1: Diagram illustrating how autonomic dysreflexia occurs in a person with spinal cord injury. The afferent stimulus, in this case a distended bladder, triggers a peripheral sympathetic response, which results in vasoconstriction and hypertension. Descending inhibitory signals, which would normally counteract the rise in blood pressure, are blocked at the level of the spinal cord injury. The roman numerals (IX, X) refer to cranial nerves. Photo: Chesley Sheppard
