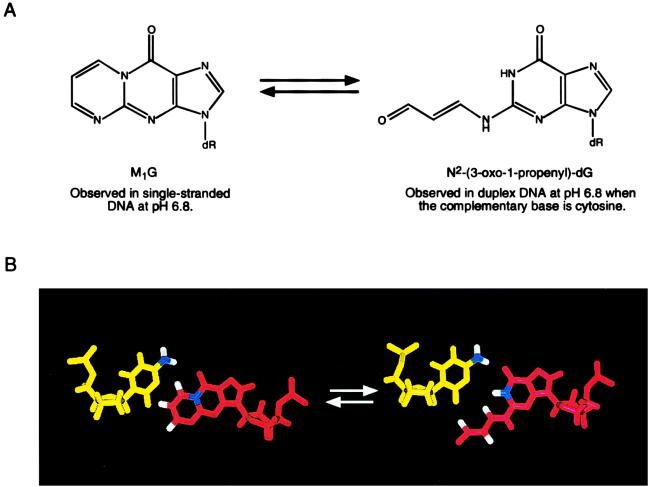
Figure 2.
(A) Analysis of d(GGTXTCCG)⋅d(CGGACACC) and d(ATCGCXCGGCATG)⋅d(CATGCCGCGCGAT) revealed that, at pH 6.8, M1G had undergone a quantitative chemical transformation into N2-(3-oxo-1-propenyl)-dG. On strand dissociation at neutral pH, M1G was regenerated. (B) Molecular modeling revealed that the exocyclic N4 amino group of the complementary cytosine was positioned in duplex DNA to catalyze opening of M1G, probably via attack at the C8 position of M1G.