Figure 2.

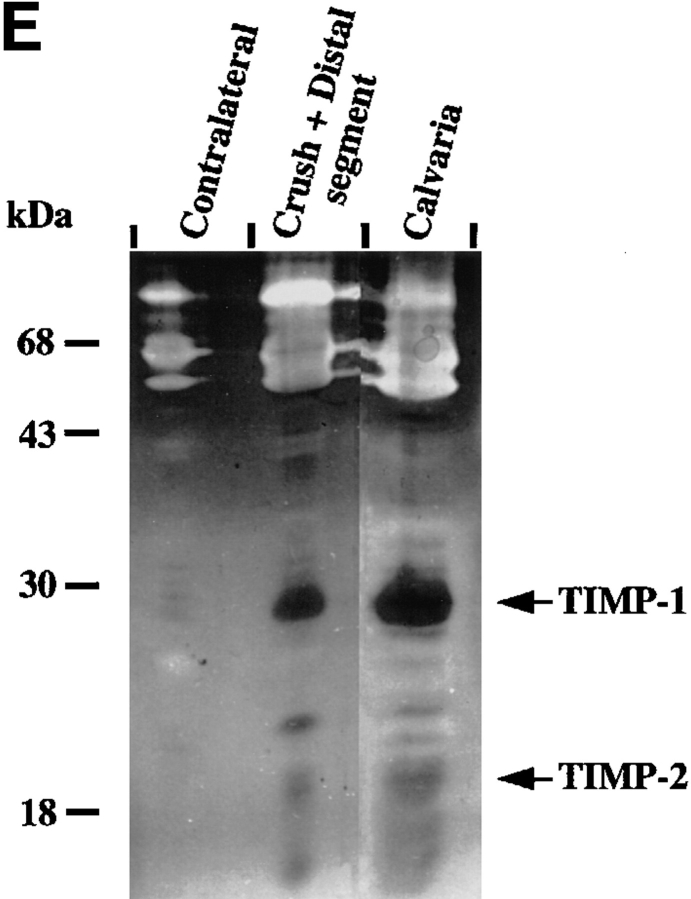
MMPs and TIMPs in normal and injured sciatic nerve. (A) Uninjured contralateral nerve, sham-operated nerve, and injured nerve at 1 and 4 d post-crush were dissected and cut into segments as described in Materials and Methods. Tissue extracts (20 μg/ lane) prepared from segments of contralateral nerve and proximal-crush-distal segments of injured nerve were assayed for gelatin-degrading activity by SDS–substrate gel zymography. Samples were treated with (+) or without (−) APMA for 1 h to partially activate latent MMP activity before electrophoresis. After electrophoresis, the gel was cut, and a portion of the gel was incubated either with (+) or without (−) 50 μM GM6001, an inhibitor of MMP activity. Clear (white) bands indicate proteolytic activity. Migration of gelatinase A (gel A) and gelatinase B (gel B) is indicated on the right, and molecular weight markers are indicated on the left. White arrows next to gelatinolytic bands in the crush segment indicate, from top to bottom: gelatinase B aggregates, 135-kD gelatinolytic band, progelatinase B, active gelatinase B, and progelatinase A. (B, top) Total RNA (100 ng) from the distal segment of injured nerve at 4 d after crush (open squares) or contralateral uninjured nerve (filled circles) was reverse transcribed, and equal amounts of cDNA were amplified by PCR. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of gelatinase B was performed by sequentially removing aliquots of the reaction mix after various numbers of cycles for each sample. For determination of the difference in transcript levels, two points (corresponding to equal amounts of input RNA or cDNA) within the exponential range of the curve were compared. (B, bottom) An example of the ethidium bromide–stained bands. (C) Segments of uninjured contralateral and 4-d postcrush nerve were cultured for 24 h, and the serum-free CM was separated on a nondenaturing SDS–polyacrylamide gel, transferred to membranes, and analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti–stromelysin-1 antibody. Prostromelysin-1 was detected in unconcentrated medium for all samples. As a positive control to show migration of prostromelysin-1 and active stromelysin-1, CM collected from a 24-h culture of mouse calvaria was incubated with APMA for 1 h. Equivalent volumes of CM per milligram of wet weight were loaded per lane. Molecular weight markers are indicated on the left. These experiments were performed on 2–4 nerves. (D) Degradation of 14C-labeled gelatin in solution was used to show the presence of endogenous MMP inhibitors in nerve extracts from pooled crush and distal segments of injured nerve. Various amounts of nerve extract (filled squares, contralateral; filled circles, crush) or recombinant human TIMP-1 (open circles) were incubated with 100 nM purified gelatinase B, followed by the addition of 14C-labeled gelatin substrate. After incubation, solubilized 14C-labeled products were determined. Results represent the mean ± range of two experiments. CM from calvaria (filled triangles), a rich source of TIMP-1, was used as a positive control. (E) Segments of uninjured contralateral and 4-d postcrush nerve were cultured for 24 h, and MMP inhibitory activity secreted in the serum-free CM was assayed by reverse zymography. CM collected from a 24 h culture of mouse calvaria served as a control. CM was concentrated 50-fold by quinine sulfate precipitation. Equivalent volumes of CM per milligram wet weight of nerve were loaded per lane. Clear (white) areas indicate proteolytic activity, and dark areas indicate MMP inhibitory activity. Molecular weight standards are indicated on the left and migration of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 standards on the right. (F) Expression of TIMP-1 and gelatinase B mRNA in sciatic nerve at 1 and 4 d after crush. Total RNA (10 μg) from segments of uninjured contralateral nerve and proximal, crush, and distal segments of injured nerve at 1 and 4 d after crush was prepared for RNA blot analysis. RNA isolated from contalateral nerve at 1 and 4 d after crush was pooled, as was the RNA from the proximal segment of injured nerve. (Upper panel) The blot was hybridized with the following cDNA probes: TIMP-1, gelatinase B, and 28 S RNA. The blot was exposed 7 d for TIMP-1 and 10 d for gelatinase B. (Lower panel) Quantification of the mRNA signals shown was obtained by scanning of the probed blots in a PhosphorImager. The values obtained for TIMP-1 and gelatinase B in contralateral nerve was set equal to 1. Values were normalized against the value obtained for the 28 S RNA hybridization to correct for differences in loading of the different RNA samples, and are shown as fold induction, which is the ratio of mRNA in crush and distal segments of injured nerve to that of the contralateral nerve.