Figure 1.
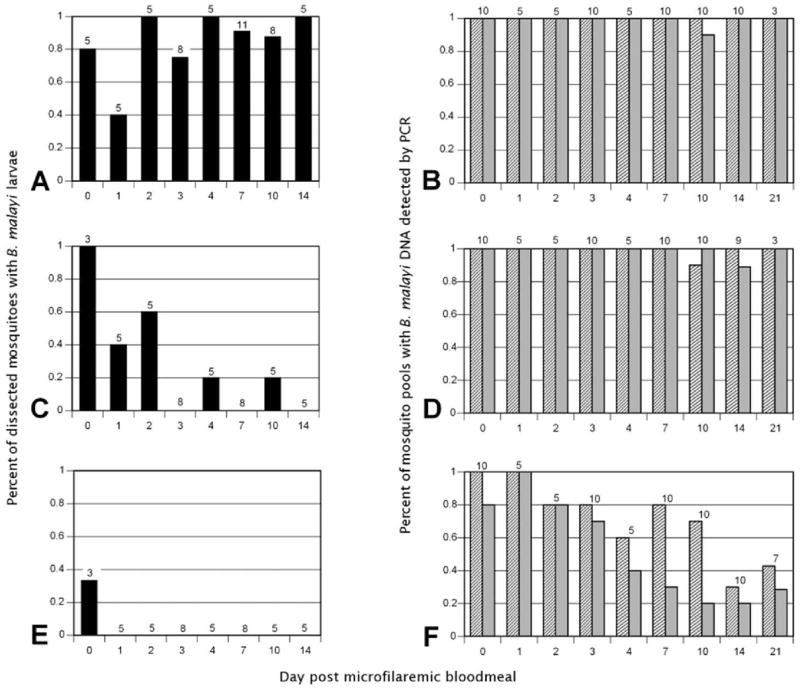
Detection of Brugia malayi in mosquito vectors. Membrane feeders containing microfilaremic cat blood were used to feed Aedes aegypti Liverpool (competent vector; A and B), Ae. aegypti Rockefeller (non-competent vector; C and D) and Culex pipiens (non-competent vector; E and F). Brugia malayi was detected by dissection of individual mosquitoes (black bars; A, C, and E) or by DNA detection using TaqMan real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (gray bars) and MGB Eclipse real-time PCR (striped bars) with DNA isolated from mosquito pools (B, D, and F). Numbers above bars indicate individual mosquitoes dissected (A, C, and E) or mosquito pools tested (B, D, and F).
