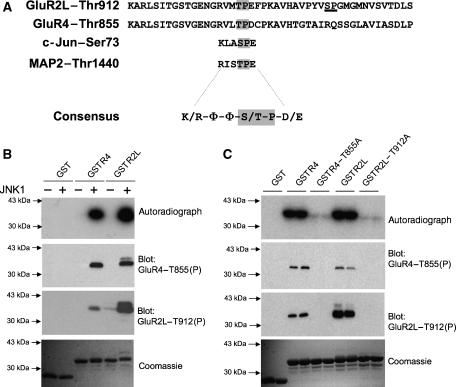
Figure 1.
JNK1 phosphorylates a novel site on AMPA-R C-terminal tails in vitro. (A) GluR2L and GluR4 sequences, from the GluR4 phosphorylation site Ser842 to the C-terminus, are aligned to indicate conserved potential MAPK phosphorylation sites (GluR2L-Thr912, GluR4-Thr855, shown in gray). These sequences show clear homology to sites on the JNK substrates cJun and MAP2 that are phosphorylated in vivo. A consensus (basic residue at N−3, aliphatic/polar/uncharged residues (Φ) at N−2 and N−1, proline at N+1, acidic residue at N+2, where N is the phosphorylated residue) is shown. A second potential MAPK site (Ser926) in GluR2L is underlined. (B) JNK1 phosphorylates GluR2L and GluR4 C-termini in vitro. Autoradiograph (top), immunoblots with GluR2LThr912(P) antibody (second panel) or GluR4Thr855(P) antibody (third panel) and Coomassie Blue staining (bottom) of purified GST, GST-GluR4 or GST-GluR2L used in kinase assays in the presence (+) or absence (−) of active JNK1. (C) JNK1 phosphorylates GST-GluR4 and GST-GluR2L at Thr-855 and Thr-912, respectively. GST, GST-GluR4, GST-GluR2L and point mutants (Thr-Ala) of these GluRs at the potential JNK phosphorylation site were incubated with active JNK1 and [γ]32P-ATP. Autoradiograph (top), GluR2LThr912(P) immunoblot (second panel), GluR4Thr855(P) immunoblot (third panel) and Coomassie Blue staining (bottom) of duplicate determinations per condition.