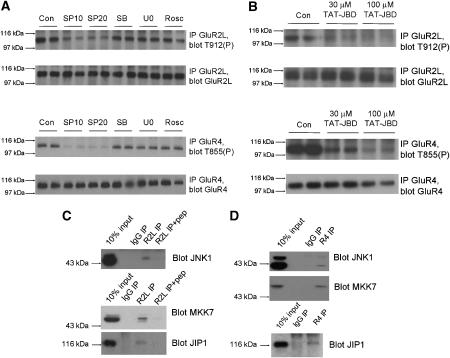
Figure 3.
JNK-JIP1 complexes mediate high basal phosphorylation of GluR2L-Thr912 and GluR4-Thr855 in neurons. (A) Cortical neurons (DIV 15–20) were washed into aCSF containing DMSO vehicle control (‘Con') or the indicated inhibitors (SP10: 10 μM SP600125; SP20: 20 μM SP600125; SB: 10 μM SB 203580; U0: 10 μM U0126; Rosc: 10 μM Roscovitine) prior to lysis. GluR2L immunoprecipitates were blotted for phosphoThr912 (Top) and GluR2L (second panel). GluR2L-Thr912 phosphorylation relative to total GluR2L signal (normalized to control, 100%): SP10: 53.5±5.4%, N=6; SP20: 35.4±5.4%, N=6; SB: 95.7±18.2%, N=5; U0: 89.8±18.2%, N=6; Rosc: 86±24.5%, N=5). GluR4 immunoprecipitates were blotted for phosphoThr855 (third panel) or GluR4 (bottom). GluR4-Thr855 phosphorylation relative to total GluR4 (normalized to control, 100%). SP10: 19.8±3.9%; SP20: 24.2±2.9%; SB: 93.7±9.1%; U0:86.9±4.8%; Rosc: 102.7±12.1% (N=4 for all treatments). (B) as A except that neurons were incubated for 1 h with the indicated concentrations of TAT-JBD peptide. (C) GluR2L immunoprecipitates (pre-incubated with or without antigenic peptide) were prepared from membrane fractions from juvenile (P17–20) rats and blotted for JNK pathway components. (D) As (C) except that GluR4 immunoprecipitates were prepared.