Figure 2.
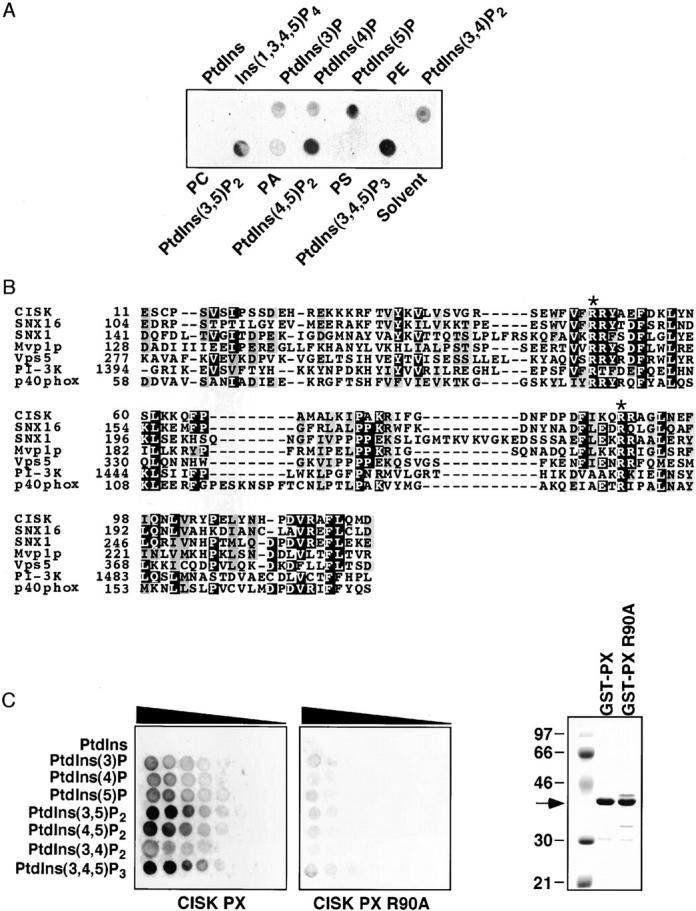
The CISK PX domain can specifically bind phosphoinositides. (A) The ability of the CISK PX domain to bind lipids was tested by a protein/lipid overlay assay using GST-CISK PX domain fusion proteins and nitrocellulose-immobilized phospholipid strips (100 pmole/spot). PtdIns, phosphatidylinositol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine. (B) Sequence alignment of the PX domains from CISK, SNX16, SNX1, Mvp1p, Vps5, PI-3 kinase, and p40phox. Asterisk indicates conserved Arg residues. (C) The lipid binding abilities of the wild-type (left) and mutant (R90A; middle) CISK PX domain were examined using nitrocelluose-immobilized phosphoinositide arrays (100–1.6 pmole/spot with twofold dilution). The triangles indicate decreasing concentration. The expression of the GST fusion proteins is shown on the right.
