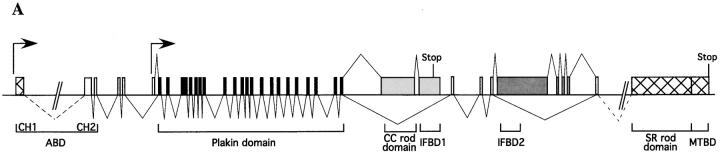
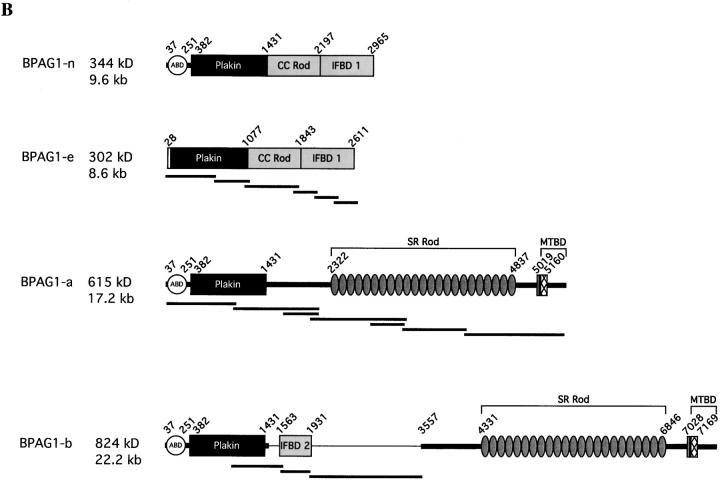
Figure 1.
The genomic structure of BPAG1 and the predicted architecture of BPAG1 isoforms. (A) The structure of the 5′ portion of BPAG1 gene is illustrated. The putative promoters are indicated by arrows. The plakin domain is encoded by 21 exons (black), whereas the CC rod domain and the IFBD1 are each coded by a single exon (light gray). The dark gray boxes represent exons specific for BPAG1-b that contain the IFBD2. Exons and cDNA (hatched boxes) that harbor a stop codon are marked. (B) Schematic representation of the domain structure of BPAG1 isoforms. The names of BPAG1 isoforms, their predicted molecular masses, and the length of their composite cDNAs are indicated. Bold lines underneath the schematic protein drawings represent nested PCR products. The names of individual domains are indicated, except for the EF-hand calcium binding motifs (small gray boxes) and the MT-binding Gas-2–related domain (hatched boxes). The numbers of the amino acids that mark the boundaries of each domain are also shown.