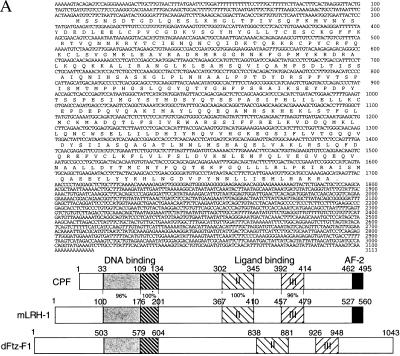
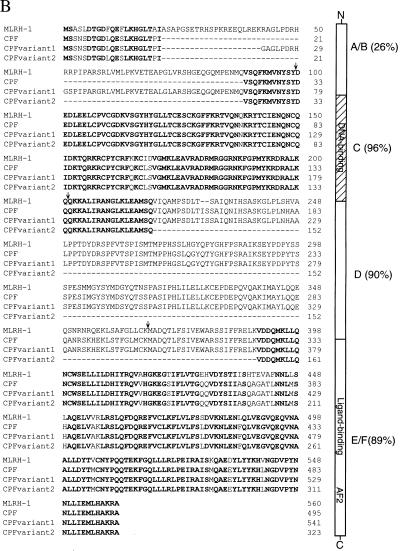
Figure 4.
(A) cDNA and predicted amino acid sequence of CPF. A human liver cDNA library was screened with a probe based on the conserved DNA-binding domain of the Drosophila Ftz-F1 nuclear receptor. Nucleotide positions are shown on the right. The predicted amino acid sequence is written in single-letter abbreviations below the nucleotide sequence. A schematic representation of CPF, mLRH-1, and dFtz-F1 is shown below the CPF nucleotide and protein sequence. We have noted that during preparation of our manuscript, a similar but shorter, cDNA sequence with an identical coding region and slightly different 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions was reported by Li et al. (41). (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of mLRH-1 and human CPF, along with CPF variants 1 and 2. The amino acids conserved among all four clones are highlighted in bold. The structural/functional domains of CPF are illustrated to the right of the alignment with percent identity to mLRH-1 in parenthesis. A/B: N-terminal variable region; C: DNA-binding domain; D: Variable hinge region; E/F: Ligand-binding domain. Arrows above the sequence alignment indicate boundaries of the domains.