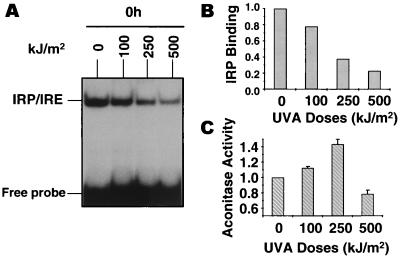
Figure 1.
(A) Modulation of IRP-1/IRE-binding activity 0 h after irradiation of human FEK4 fibroblasts with UVA doses of 100, 250, and 500 kJ/m2. The positions of the IRP/IRE complexes and of excess free probe are indicated. (B) The IRP/IRE signals of irradiated cells (from A) were quantified and their relative intensities normalized against that of nonirradiated control (in A) and expressed as a fold increase in IRP-1-binding activity above control value as a function of UVA dose. (C) The effect of UVA exposure on aconitase activity in IRP-1 (B) after UVA irradiation in FEK4 cells exposed to doses up to 250 kJ/m2. The aconitase activity of irradiated samples (mean ± SD) were expressed as a fold increase in aconitase activity compared with that of unirradiated controls (0 kJ/m2) as a function of UVA doses. n = 4–6 independent experiments in which three measurements have been performed.