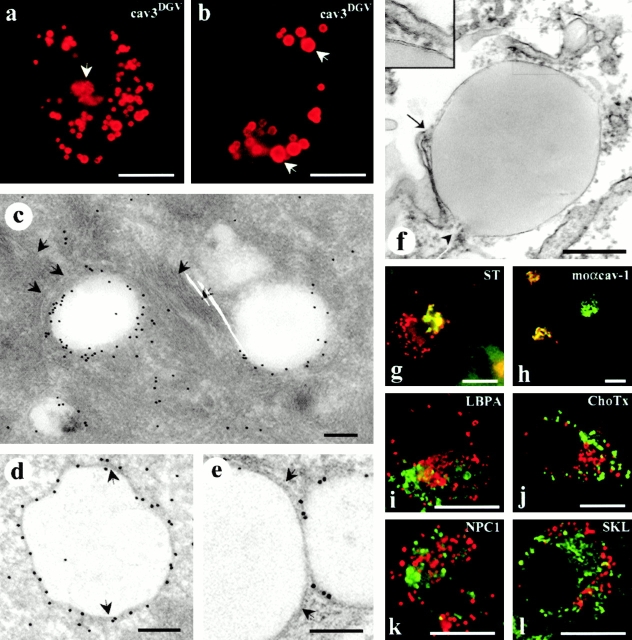
Figure 1.
CavDGV is targeted to the membrane of intracellular vesicular structures. a, BHK cells were transfected with HA-tagged cav-3DGV for 24 h and were then labeled with antibodies to HA tag, followed by specific Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies. CavDGV mainly located in enlarged intracellular rings, and some protein was detected in the tubular elements of the ER (see Fig. 2) and in the perinuclear region (arrows and g and h). b, BHK cells were transfected with HA-tagged cavDGV for 24 h and were then treated with 5 μg/ml of cycloheximide for an additional 24 h. After blocking of protein synthesis, the truncated protein was exclusively detected in very enlarged intracellular vesicles (arrows). c, BHK cells were transfected with GFP-tagged cavDGV and frozen sections were processed for immunoelectron microscopy using anti-GFP antibodies, followed by protein A–gold. The mutant protein was detected enriched on the membrane of electron-lucent vesicles of 300–500-nm diam, often surrounded by intermediate filaments (arrows). d and e, Lowicryl sections (of freeze-substituted/low temperature embedded sections) of GFP-tagged cavDGV-transfected cells labeled with antibodies to GFP followed by protein A–gold. CavDGV-containing vesicles (CDV) comprise a membrane bilayer (see arrows in d and e) surrounding a putative lipid-filled area. f, Epon sections showing a morphologically similar structure connected to tubular elements possibly corresponding to the ER (arrow and arrowhead), which were frequently observed in nontransfected cells. The typical morphology of lipid-filled body enclosed by a bilayer structure (see insert) is readily observed in epon sections. g, BHK cells were cotransfected with myc-tagged sialotransferase (a specific marker for trans Golgi) and HA-tagged cavDGV and the distribution of the proteins studied by immunofluorescence by means of antitag specific antibodies. The distribution of sialotransferase (green) and cavDGV (red) clearly overlapped in the Golgi area, however CDV rings did not contain the Golgi marker. h, HA-tagged cavDGV-transfected cells were label with an mAb to cav-1 (which exclusively recognizes the Golgi complex conformation of cav-1) and a polyclonal antibody to HA-tag. When cavDGV (red) accumulated in the Golgi region, the truncated protein clearly colocalized with the Golgi complex-associated pool of endogenous cav-1 (green). i and l, HA-tagged cavDGV-transfected cells were labeled with polyclonal antibodies to the peroxisome marker SKL (l) or the late endosome marker, lysobisphosphatidic acid (h) and with an mAb to the HA-tag. The endosome and peroxisome markers (green) were excluded from the CDV compartment (red). j, CavDGV-transfected cells were incubated for 2 h at 37°C with 10 μg/ml of GM1 to allow insertion of the ganglioside into the plasma membrane and internalization. GM1, detected by using 1 μg/ml of Cholera toxin–FITC, was completely excluded from the CDV compartment (red). k, BHK cells were cotransfected with Niemann-Pick C1 protein and cavDGV for 24 h and were then labeled with a polyclonal antibody to NPC1 and the mAb to the HA tag. Transfected NPC1 (green) does not colocalize with the CDV vesicles (red). Bars: (a, b, and g–l) 5 μm; (c–f) 100 nm.