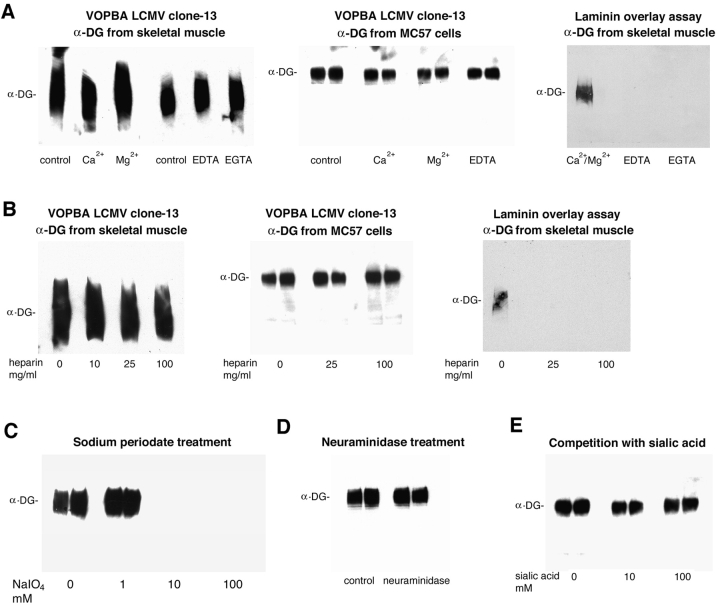
Figure 1.
Biochemical characterization of the LCMV–α-DG interaction. α-DG purified from rabbit skeletal muscle or enriched from MC57 cells was subjected to VOPBA using 107 PFU/ml of LCMV clone-13 or to laminin overlay assay with 10 μg/ml biotinylated laminin-1. Bound virus was detected using monoclonal antibodies WE33 and WE36 against LCMV-GP. For detection of bound biotinylated laminin-1, HRP- conjugated streptavidin was used. (A) The cation dependence of the binding of LCMV and laminin-1 to α-DG was tested by addition of 1 mM Ca2+, 1 mM Mg2+, 10 mM EDTA, or 10 mM EGTA. (B) For inhibition with heparin, virus or biotinylated laminin-1 were pretreated with 0, 25, and 100 mg/ml heparin before incubation with immobilized α-DG. (C) To test for a potential role of α-DG–derived carbohydrates in virus binding, α-DG from MC57 cells was pretreated with 0, 1, 10, and 100 mM sodium periodate before the addition of virus. A potential role of α-DG–derived terminal sialic acids was addressed by neuraminidase treatment (D) and competition with 0, 10, and 100 mM sialic acid (E).