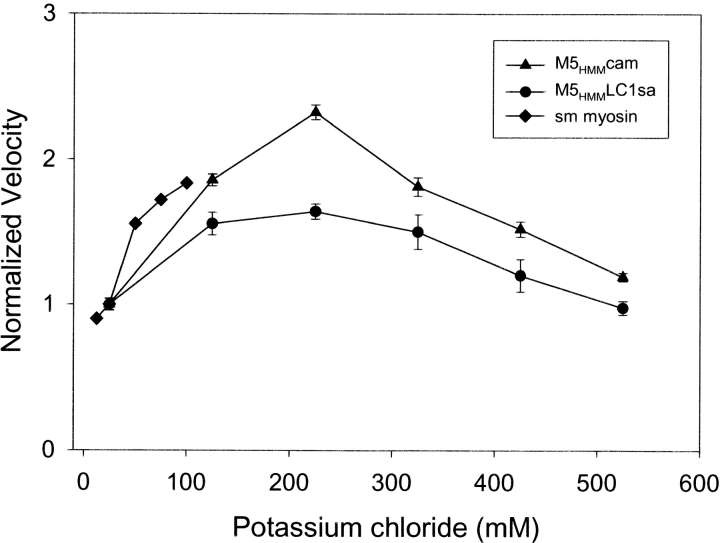
Figure 3.
The ionic strength dependence of M5 HMM in vitro motility. Normalized filament velocity (mean ±SEM, n > 10 filaments) as a function of added potassium chloride for M5HMM expressed with LC1sa (•) and calmodulin (▴) (M5HMM loading concentration of 10–25 μg/ml). Normalized filament velocity as a function of added potassium chloride for smooth muscle myosin II (♦) from Harris and Warshaw (1992) for comparison (loading concentration of 100 μg/ml). Note the reduction in actin filament velocity at potassium chloride concentrations <125 mM for both M5HMM and myosin II. Also note the plateau at physiological ionic strengths and greater (between 125 mM and 325 mM potassium chloride) for M5HMM. Velocities were normalized to the velocity at 25 mM potassium chloride. A similar dependence of actin filament velocity was observed regardless of light chain content.