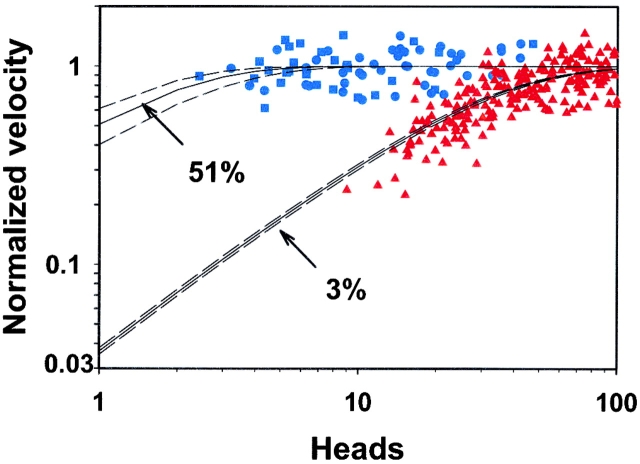
Figure 4.
The dependence of actin filament velocity on the number of interacting M5 HMM heads. Normalized filament velocity as a function the number of M5HMM heads available to interact with each filament at a loading concentration of 5 (▪) and 1 μg/ml (•). Note the independence of M5HMM-driven actin filament velocity on the number of interacting heads. The number of available heads was calculated via surface ATPase assays (described in Materials and methods). For comparison, normalized filament velocity as a function the number of smooth muscle myosin heads available to interact with each filament (▴; data from Harris and Warshaw, 1993) at a loading concentration of 10 μg/ml. (Bottom solid line) A least squares fit of the myosin II data to Eq. 1, revealing a 3% duty cycle for the myosin II data. (Top solid line) A least squares fit of the M5HMM data to Eq. 1, revealing a 51% duty cycle. Dashed lines represent the range of the fit determined by standard error of the estimate.