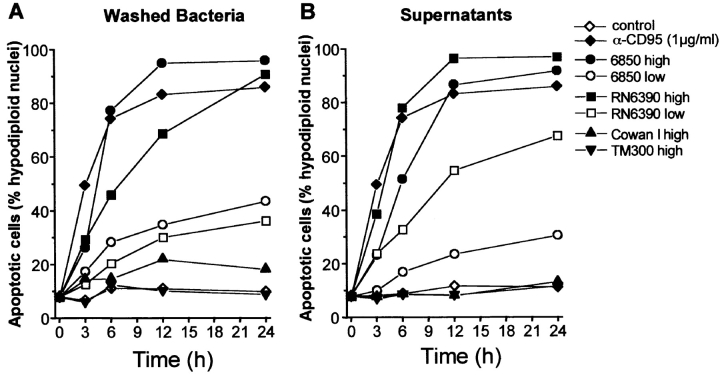
Figure 1.
Both intact S. aureus cells and bacterial supernatants induce T cell apoptosis. Jurkat cells were incubated with live washed bacteria (A) or sterile-filtered supernatants of the same bacterial cultures (B). After the indicated times, the proportion of apoptotic cells was determined by flow cytometry. (A) Fresh suspensions of the indicated bacterial strains were added to Jurkat cells, resulting in a MOI of 30 (low) and 120 (high). Cells were incubated on ice for 2 h to allow sedimentation and then shifted to 37°C. Lysostaphin (20 μg/ml) was added to lyse and kill staphylococci. Lysostaphin without bacteria served as a negative control, whereas agonistic anti-CD95 was used as a positive control. (B) Fresh bacterial supernatants were added to Jurkat cells, resulting in a final concentration (vol/vol) of 0.1% (low) and 1% (high).