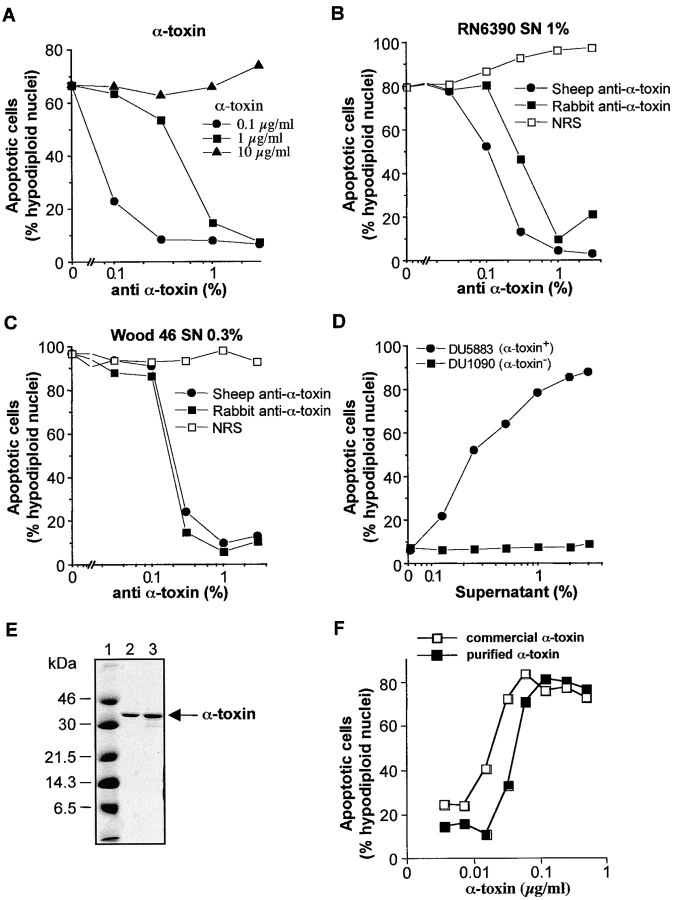
Figure 2.
S. aureusα-toxin is required for induction of apoptosis. (A) Effect of purified α-toxin. Jurkat cells were preincubated for 30 min with various dilutions of a sheep anti–α-toxin antiserum and then incubated with the indicated concentrations of the commercially available preparation of α-toxin. (B and C) Anti–α-toxin neutralizes the proapoptotic activity of S. aureus supernatants. Jurkat cells were preincubated with various dilutions of a sheep anti–α-toxin antiserum, a rabbit anti–α-toxin antiserum, or normal rabbit serum (NRS) for 30 min. Subsequently, sterile-filtered supernatants of RN6390 (B) or Wood 46 (C) were added at the indicated dilutions, and formation of hypodiploid nuclei was assessed. (D) α-Toxin–deficient S. aureus does not induce apoptosis. Jurkat cells were incubated with various concentrations of supernatants of the α-toxin–producing strain DU5883 or its α-toxin–deficient counterpart DU1090. (E) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE of a highly purified (lane 2) and the commercially available (lane 3) α-toxin preparation. The molecular sizes of the protein marker used in lane 1 are indicated on the left. (F) Jurkat cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of the two α-toxin preparations, and cell death was assessed after 24 h.