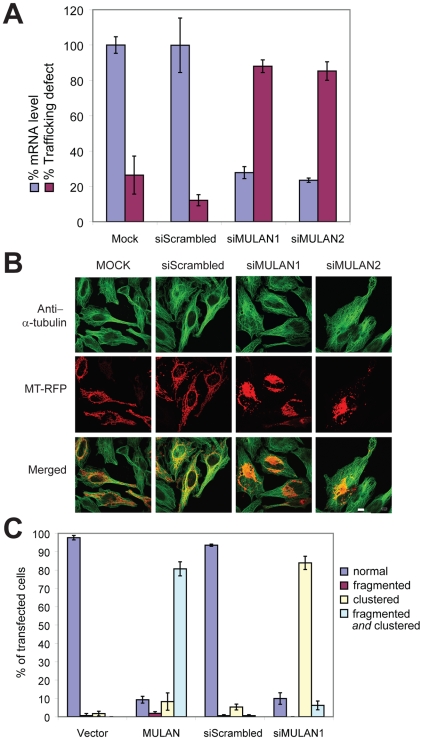
Figure 2. Knockdown of endogenous MULAN perturbs mitochondrial dynamics.
A) Blue bars: MULAN mRNA knockdown. RNA was extracted from HeLa cells 48 h after transfection with siRNA oligos targeting two different MULAN sequences, or with a negative control siRNA (siScrambled). Knockdown efficiency was determined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Results were normalized to the level of the 36B4 mRNA, which was amplified in the same multiplex reaction, as an internal control. Purple bars: MULAN knockdown leads to mitochondrial perinuclear clustering. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs on day 1, followed by MT-RFP on day 2. Cells were fixed on day 3 and the percentage of RFP-positive cells with perinuclear-clustered mitochondria was scored. B) The microtubule network is apparently intact in MULAN-knockdown cells. As in “A”, except that cells were fixed and stained with anti-α-tubulin antibody for analysis (green). C) Both MULAN ectopic expression and endogenous knockdown indicate its role in mitochondrial dynamics. For ectopic expression, HeLa cells were transfected with vector or MULAN wild type cDNA together with MT-RFP. Cells were fixed for analysis 24 h post-transfection. For siRNA-mediated knockdown, cells were transfected with siScrambled or siMULAN1 on day 1 and with MT-RFP on day 2. Cells were fixed on day 3. Mitochondrial fragmentation and clustering were quantitated under 100× field. At least 100 cells were counted per condition and data represent average of three independent transfections.