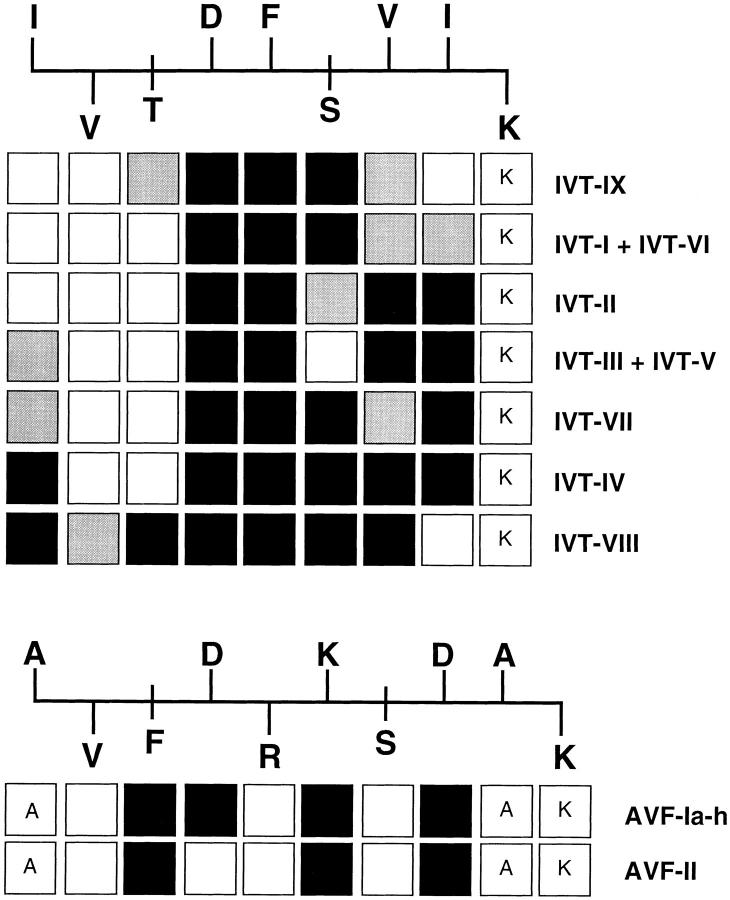
Figure 2.
Fine specificity of the various IVT and AVF-specific TCR types defined by alanine scanning mutagenesis. IVT and AVF-specific CTL clones were tested for lysis of A11+ PHA blasts pulsed with 10−9 and 10−10 M of the indicated peptide analogue. The sequence of the wild-type peptide and the predicted orientation of each residue relative to the A11 groove (20) are indicated above each Ala replacement set. Residues pointing towards the groove are shown below the peptide backbone and residues pointing towards the TCR are shown above. The putative accessory anchors are indicated crossing the backbone. Boxes below each residue indicate the corresponding Ala substituted analogue tested with clones expressing the indicated TCR type (left). When the wild-type residue is shown in the box the corresponding analogue was not tested. White boxes indicate that the analogue was recognized as efficiently as the wild-type peptide at both peptide concentrations, black boxes indicate no recognition at either peptide concentration and gray boxes correspond to at least 50% of the control lysis at a concentration of 10−9 M. Each assay was performed three times and the results obtained with individual clones were highly reproducible. All clones listed in Table 2 were tested. In several cases the screening was performed before the TCR-α/β sequences became available. Later results confirmed the absolute correlation between each TCR type and a given pattern of reactivity.