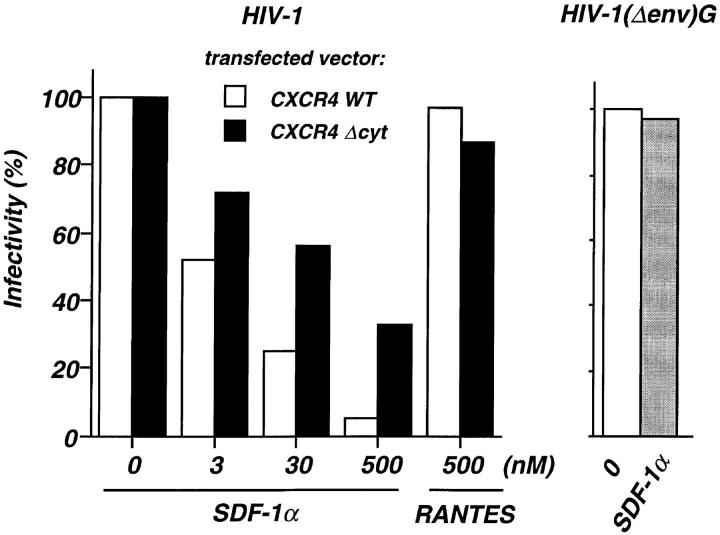
Figure 4.
SDF-1α–dependent inhibition of HIV infection in cells expressing wild-type or COOH-terminally truncated CXCR4. U373-CD4 LTRlacZ were transfected with either CXCR4 WT or CXCR4 ΔCyt expression vector, plated in 96-well plates (104 cells per well) and infected with the HIV-1NL4-3 strain or the pseudotyped HIV-1(Δenv)G, in the presence of the indicated concentrations of SDF-1α or RANTES. HIV-1(Δenv)G–infected cells were treated with 500 nM SDF-1α. Cell cultures were carried out in triplicates. Surface expression of CXCR4 WT or CXCR4 ΔCyt was assessed 24 h after transfection by FACS® analysis and amounted to 482 and 533 fluorescence units, respectively. HIV infection was revealed 24 h later by staining for β-galactosidase activity and scoring of positive cells. The numbers of HIV-infected cells per well in the absence of chemokines were 168 and 232 (mean of five experiments) for cultures transfected with CXCR4 WT and CXCR4 ΔCyt, respectively. In cultures infected with HIV-1(Δenv)G the average number of infected cells per well was 280. Shown are the percentages of infected cells in the presence of chemokines. Infection with HIV-1NL4-3 or HIV-1(Δenv)G in the absence of chemokines was set to 100%.