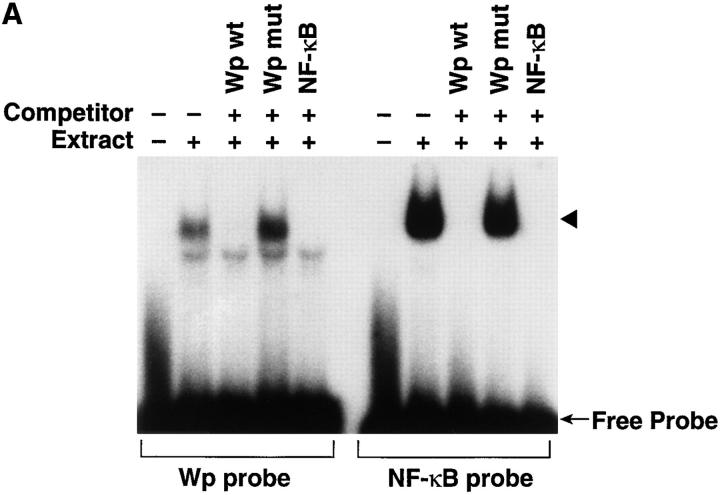
Figure 4.
NF-κB activated by EBV binding binds to and activates Wp. (A) Binding of activated NF-κB to the NF-κB–like site in Wp. Nuclear extracts from purified resting B cells 30 min after addition of EBV were evaluated for ability to bind to labeled probes duplicating the NF-κB–like site in Wp (left), or an NF-κB consensus sequence (right), by EMSA. Competition studies were carried out with unlabeled probes reflecting the wild-type Wp sequence (Wp wt), Wp bearing a mutant NF-κB–like sequence (Wp mut), or the wild-type NF-κB consensus sequence (NF-κB). (B) Transcriptional activation of Wp by NF-κB. CAT activity assays were carried out in human 293 cells cotransfected with p50, p65, or p50 plus p65 expression plasmids together with a Wp CAT reporter plasmid, a Wp CAT reporter plasmid with a mutated NF-κB site, or an HIV CAT reporter plasmid.