Figure 5.
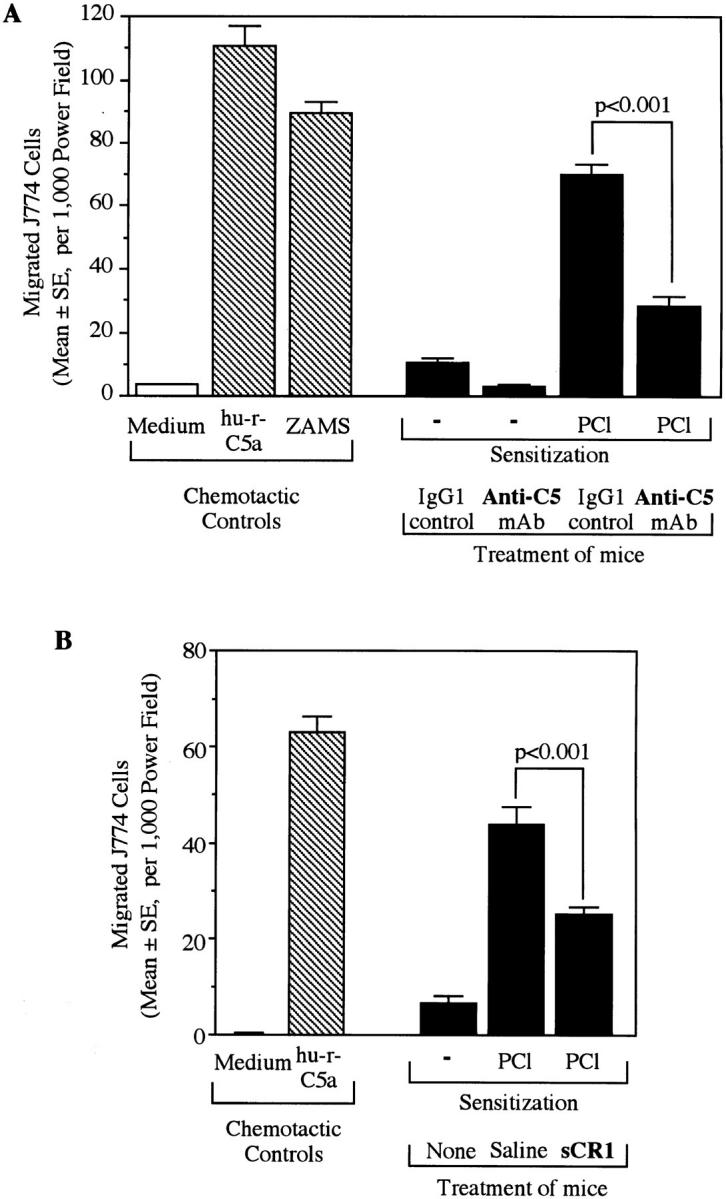
Anti-C treatment resulted in decreased chemotactic activity in 24-h CS ear extracts. Two different C inhibitors, anti-C5 mAb (A) and sCR1 (B), were used. Mice were ear challenged 4 d after PCl contact sensitization. Punch biopsies from each ear were collected 24 h later and then were extracted with PBS. In vitro chemotaxis assay was performed on the ear extracts using target J774A.1 macrophage cells which did not migrate against the RPMI 1640–0.25% gelatin medium. Human rC5a (100 ng/ml) and ZAMS (1:20) prepared from normal mouse serum were used as positive chemoattractant controls. (A) Mice were injected i.v. 24 and 4 h before ear challenge with either anti-C5 (1 mg/mouse) or with isotype (IgG1) matched control anti–human C8 (1 mg/mouse). (B) Mice were injected i.p. with 125 μg/mouse sCR1 30 min before ear challenge.
