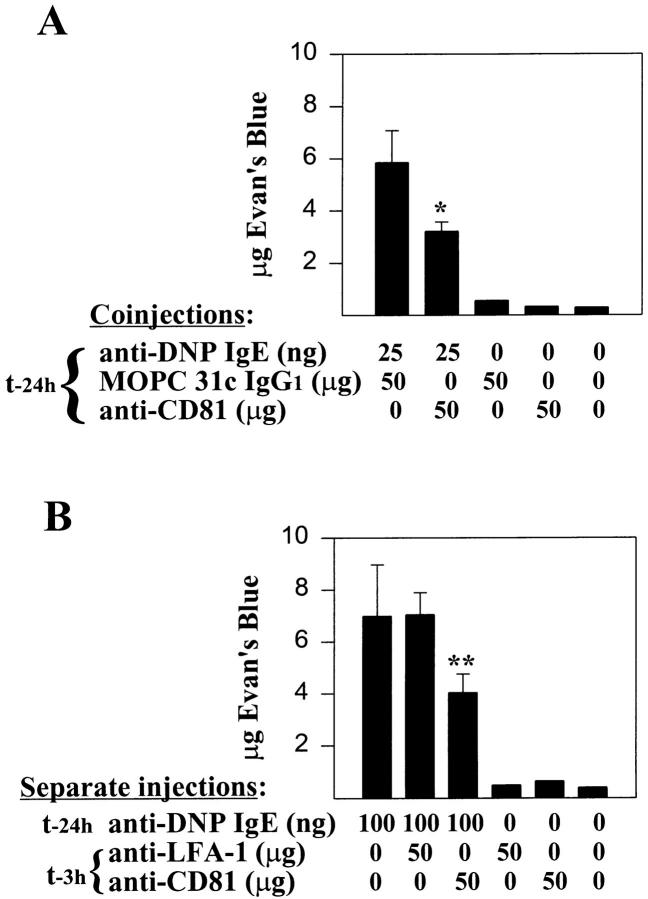
Figure 4.
Inhibition of passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in Wistar rats by anti-CD81. Male Wistar rats were injected intradermally with (A) 25 ng DNP-specific IgE mixed with 50 μg anti-CD81 mAb 5D1 (mouse IgG1) or control mouse IgG1 mAb (MOPC 31c; specificity unknown) or (B) 100 ng DNP-specific IgE alone. Mice receiving 100 ng IgE alone were reinjected 21 h later with buffer, 5D1, or a mouse IgG1 control mAb to LFA-1β chain (anti-CD18; WT.3). Control sites (no IgE) received buffer or 50 μg of IgG1 subclass mAb. 24 h after IgE injections, 1 mg of antigen (DNP–HSA; 1 mg/ml in PBS containing 1% Evan's blue dye) was injected intravenously and rats were killed 30 min later. Extravasation of Evan's blue dye into the skin was quantified by A610 measurements of serial hot formamide extractions (54) of minced punch biopsies (2.5 cm2/ site). Sample A610 values were converted to micrograms of Evan's blue dye based on standard curves of Evan's blue A610 absorbance in formamide. Results taken from three injected sites per condition (IgE plus buffer or antibody) or a single site (IgG1 controls without IgE) from a single rat and expressed as mean micrograms of Evan's blue dye ± standard deviation. Comparable results were obtained on two additional rats for both experiments shown. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired Student's t test: *, P <0.05; **, P <0.01 (actual values: A, P = 0.024 versus MOPC 31c controls; B, P = 0.009 versus anti-LFA-1β controls).