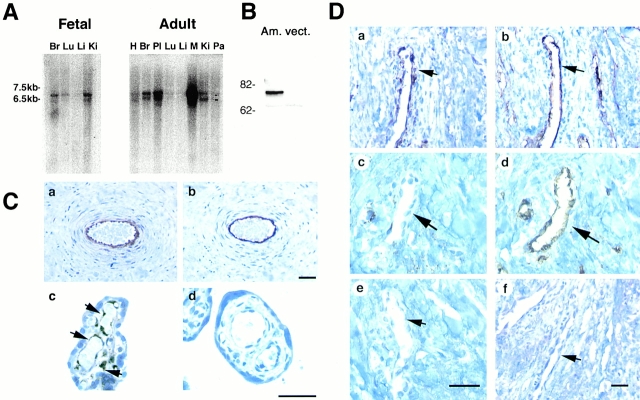
Figure 4.
Angiomotin is expressed in endothelial cells in vivo. (A) Northern blot analysis of angiomotin expression in fetal and adult human tissues. 2 μg of poly A+ RNA was analyzed for expression of angiomotin using a 1-kb probe from the 5′ region. Two detectable transcripts were detected in both fetal and adult tissues (multitissue blot from CLONTECH Laboratories, Inc.; H, heart; Br, brain; Pl placenta; Lu, lung; Li, liver; Ki, kidney; Pa, pancreas; M, marker). (B) Western blot analysis using immunoaffinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibodies against angiomotin. The antibodies detected a band with an approximate molecular mass of 75 kD in angiomotin-transfected NIH 3T3 (Am.) cells but not in the vector (vect.) control. (C) Immunohistochemical localization of ABP-1 protein in human placenta. Paraffin-embedded placental tissue from term placenta was stained with immunoaffinity-purified angiomotin polyclonal antibodies. (C, a) Shows angiomotin protein in endothelium of larger vessels in a placental villus. (C, b) Immunostaining using a monoclonal antibody against CD34, an endothelial marker. (C, c) Detection of angiomotin protein in capillaries of placental microvilli. (C, d) IgG negative control. (D) Expression of angiomotin in a dermal Kaposis sarcoma. (D, a) Shows angiomotin staining of a blood vessel within the Kaposis lesion. (D, b) CD34 staining of a consecutive section of D, panel a. (D, c) Angiomotin-negative dermal blood vessel (arrow) in the normal tissue adjacent to the Kaposis lesion. (D, d) Same as D, panel c, but stained with CD34. D, panels e and f, are negative controls stained with nonimmune rabbit IgG as a negative control. Bars, 40 μm.