Figure 7.
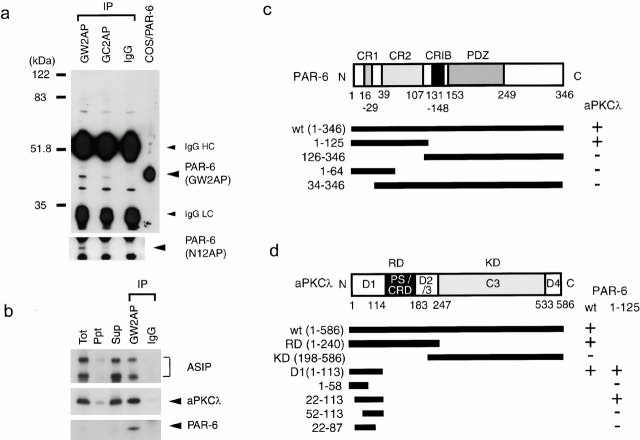
Identification of endogenous PAR-6 and its association with aPKCλ and ASIP in fully polarized epithelial cells. (a) Identification of endogenous PAR-6 protein in MDCK II cells. Semi-confluent MDCK cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with 1 μg of affinity-purified anti–PAR-6 rabbit polyclonal antibodies (GW2AP, GC2AP) or control normal rabbit IgG. The resultant immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot analysis using the antibodies indicated in parentheses (right). GW2AP and GC2AP specifically immunoprecipitate a 43-kD protein comigrating with PAR-6 expressed in COS cells, which was recognized by N12AP as well as GW2AP. (b) Ternary complex formation of PAR-6, aPKCλ, and ASIP/PAR-3 in vivo. Anti–PAR-6 (GW2AP) immunoprecipitate (IP), prepared as in a, was analyzed using anti–aPKCλ monoclonal or anti–ASIP polyclonal antibody. PAR-6 immunoprecipitates specifically contain endogenous aPKCλ, full-length ASIP, and its splicing variant (bottom band). (c and d) Summary of the yeast two-hybrid assays to analyze the PAR-6–aPKCλ interaction. The interaction was examined by growth on culture plates lacking histidine. The NH2-terminal region including CR1 and 2 of PAR-6 is sufficient for the interaction with aPKCλ (c), while NH2-terminal residues 22–113 of aPKCλ are sufficient for the interaction with PAR-6 (d).