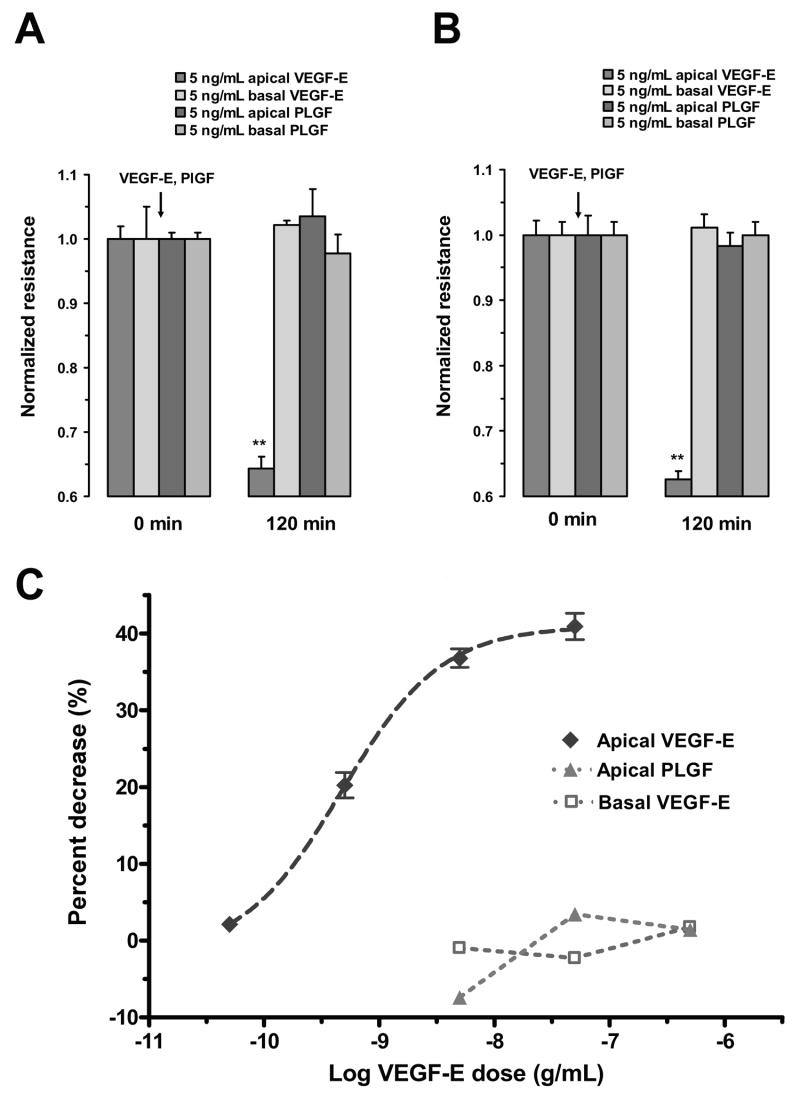
Figure 5.
Responses of RPE monolayers following VEGF-E and PlGF administration. In both ARPE-19 cells (A) and porcine primary RPE cells (B), apically administered VEGF-E (5 ng/mL) significantly reduced TER; however, apically-administration of PlGF (5 ng/mL) did not significantly alter resistance. The administration of either agonist to the basolateral side did not significantly alter TER. C, Concentration-response curves of the ARPE-19 cells to apical VEGF-E and PlGF and basal VEGF-E. The apical administration of VEGF-E induced a concentration dependent decrease in TER. The EC50 to this response was 474 pg/mL (LogEC50 = -9.32 ±0.04). The Hill coefficient was not significantly different from 1.0. Apically-applied PlGF or basolaterally-applied VEGF-E were not effective in significantly altering TER. Values are means ±SE normalized to the average resistance at t = 0. (** P <0.01)