Figure 7.
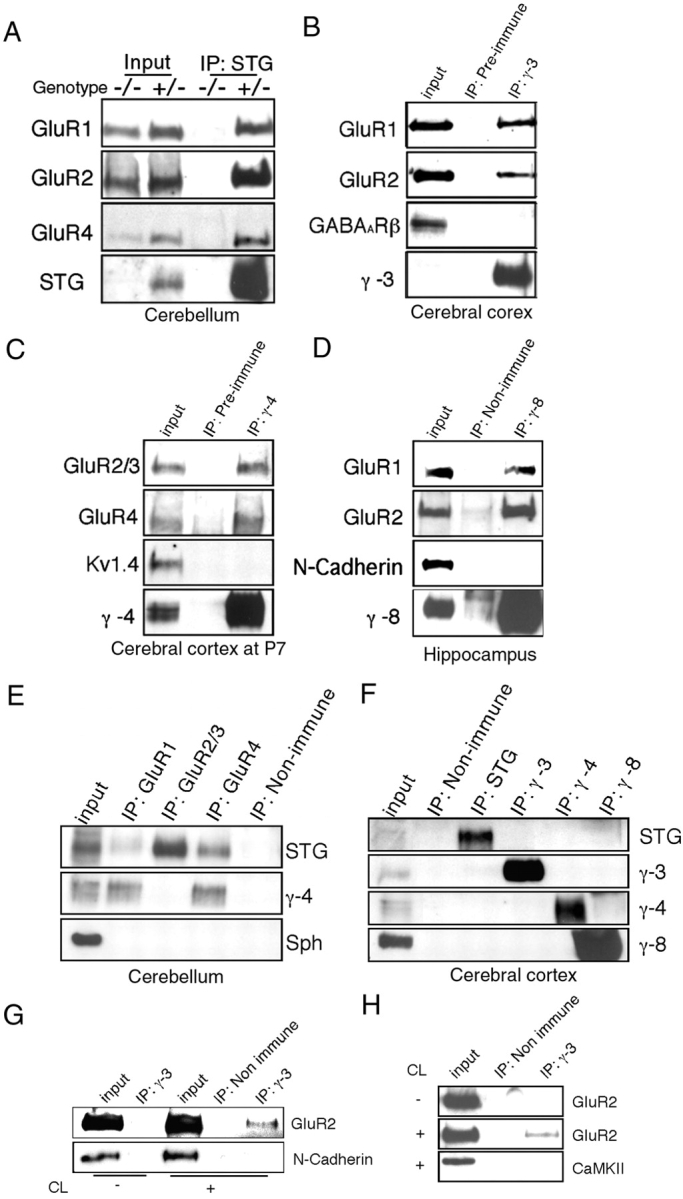
TARPs interact specifically with AMPA receptors in brain extracts. (A) AMPA receptor subunits GluR1, GluR2, and GluR4 coimmunoprecipitate with stargazin (STG) in brain extracts from +/stg mice (+/−). In extracts from stg/stg mice (−/−), the antistargazin antibody does not immunoprecipitate GluR1, GluR2, or GluR4. (B–D) AMPA receptor subunits also coimmunoprecipitate with γ-3, γ-4, and γ-8 in extracts from adult cerebral cortex, postnatal day 7 cerebral cortex, and hippocampus, respectively. As control, other transmembrane proteins such as GABAARβ, N-cadherin, and Kv1.4 did not coimmunoprecipitate. (E) Subunit specificity for TARP interactions in cerebellum. Stargazin (STG) and γ-4 coimmunoprecipitate with GluR1 and GluR4, but only stargazin coimmunoprecipitates with GluR2/3 in cerebellum. (F) TARP isoforms are strictly segregated, since they do not coimmunoprecipitate with one another in cerebral cortex. (G) Surface GluR2 coimmunoprecipitates with γ-3. Primary cerebrocortical cultures were incubated with a membrane impermeable cross-linker (CL), and after SDS solubilization extracts were immunoprecipitated for γ-3; GluR2 coprecipitates with γ-3 in a cross-linker–dependent fashion, whereas another synaptic transmembrane protein, N-cadherin, does not. H, GluR2 coimmunoprecipitated with γ-3 in chemical cross-linked PSD fractions from brain, whereas another PSD protein, CaMKII, does not.
