Figure 1.
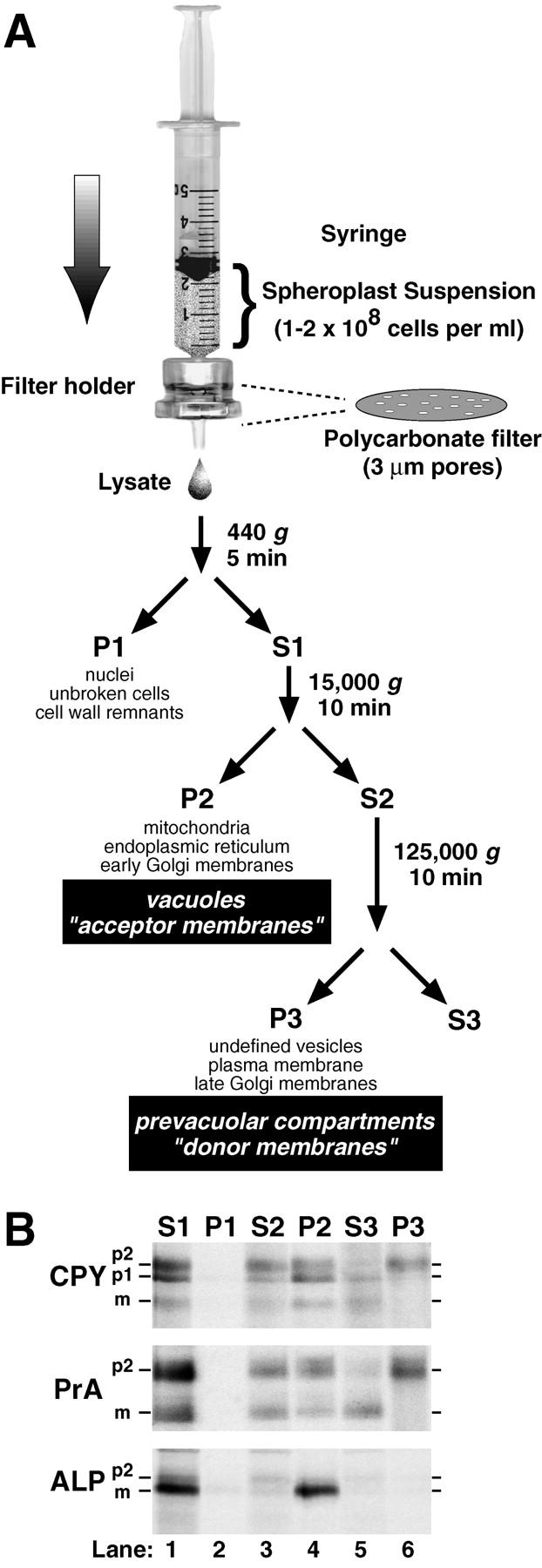
Lysis of yeast spheroplasts via extrusion through a polycarbonate filter. (A) Schematic diagram for polycarbonate filter lysis and subsequent differential centrifugation. After pushing a yeast spheroplast suspension in a syringe through a polycarbonate filter with 3-μm pores, the crude cell lysate was subjected to differential centrifugation using the indicated g forces and times. The P1, P2, and P3 pellets were enriched in the indicated organelles. (B) Fractionation of vacuolar marker proteins. Wild-type yeast spheroplasts (SEY6210) were radiolabeled with Tran35S-label for 5 min and chased with methionine and cysteine for 2 min at 30°C. The cells were subjected to lysis through a polycarbonate filter with subsequent differential centrifugation. Each supernatant and pellet from the 440 (S1 and P1), 15,000 (S2 and P2), and 125,000 g (S3 and P3) centrifugation steps was sequentially immunoprecipitated with antisera against carboxypeptidase Y (CPY), proteinase A (PrA), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). Each immunoprecipitate was subjected to SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The mid and late Golgi complex–modified precursor zymogen is designated p2, the endoplasmic reticulum and early Golgi complex precursor is designated p1 (CPY only), and the mature hydrolase is designated m for each protein.
