Figure 2.
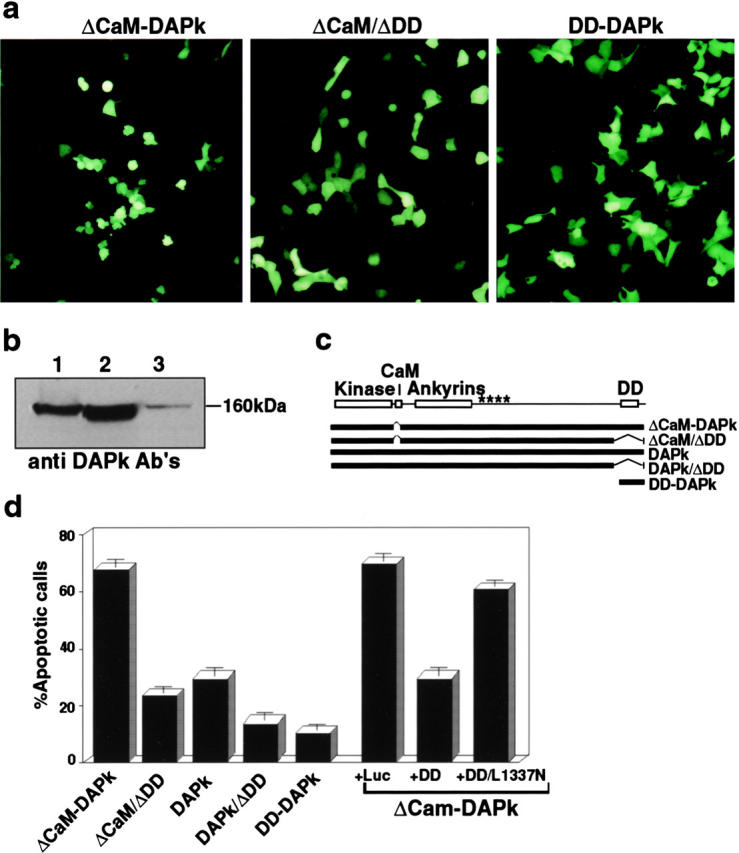
The death domain of DAP-kinase is important for its function in apoptosis. (a) Transient transfections of 293 cells with ΔCaM mutant, ΔCaM/ΔDD mutant, or with the DD-DAPk. Photographs were taken 24 h after transfection under fluorescent light microscope to visualize GFP positive cells. (b) Expression of ΔCaM and ΔCaM/ΔDD mutants in the transiently transfected 293 cells. Lane 1, expression of ΔCaM-DAPk; lane 2, expression of ΔCaM/ΔDD-DAPk; and lane 3, endogenous DAPk in cells transfected with a nonrelevant vector. Western blotting analysis was done with anti–DAP-kinase antibodies. (c) Schematic presentation of DAP-kinase mutant proteins used in these experiments. Kinase, kinase domain; CaM, calmodulin binding and regulatory domain; ankyrin, ankyrin repeats; and DD, death domain. Asterisks delineate the region that by deletion mapping was shown to be responsible for cytoskeletal binding. (d) Transfections as shown in a, with the indicated constructs or double transfections of ΔCaM mutant with the indicated constructs. The percentage of apoptotic cells was calculated as described in Materials and Methods.
