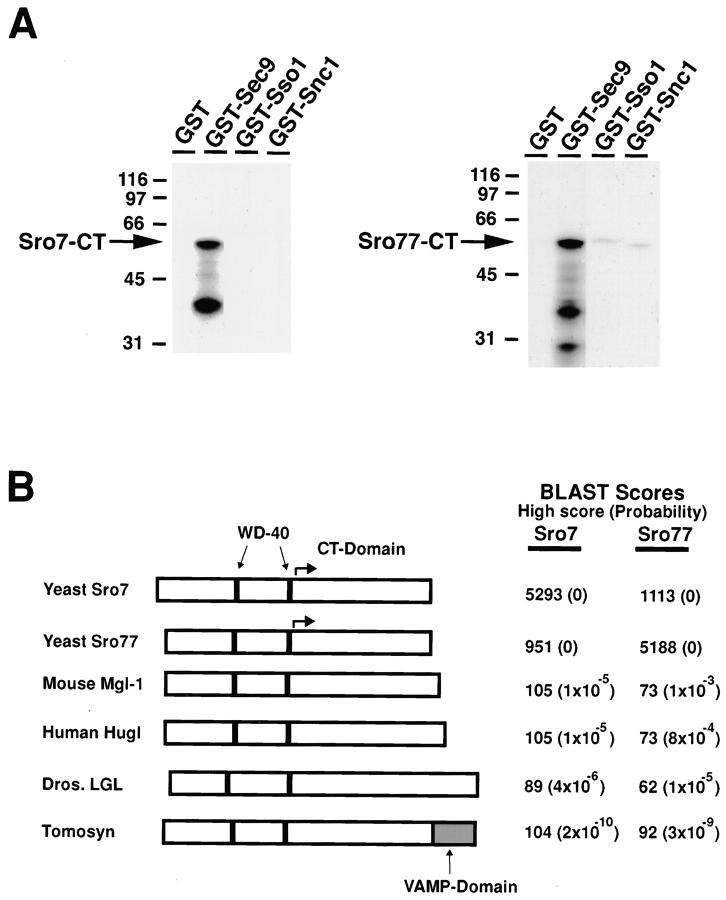
Figure 1.
Identification of Sro7p and Sro77p as Sec9p-binding proteins. (A) Interaction of in vitro translated COOH-terminal domains of Sro7 and Sro77p with Sec9p. The COOH-terminal domain of Sro7p (left) identified in the two-hybrid screen and the homologous region of Sro77p were radiolabeled by coupled transcription/translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. In vitro translation reactions were incubated with various recombinant SNARE proteins immobilized on GST beads (each at ∼1 μM in the binding reaction), washed, and the bound material was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The positions of molecular mass markers (expressed in kD) are indicated on the left of the gels. The bands corresponding to primary translation products of Sro7-CTp and Sro77-CTp are indicated by arrows. The lower molecular mass band presumably represents breakdown products. (B) Alignment of Sro7p and Sro77p with three lethal giant larvae family members and tomosyn: mouse LGL (MgCl-1, GenBank accession number D16141), human LGL (Hugl, GenBank accession number X86371), and Drosophila LGL (lg(2)l, Swiss protein accession number P08111) and tomosyn (accession number U92072). Each rectangle is drawn proportional to the length of each coding sequence. The positions of the predicted WD-40 repeats and the VAMP-like domain are indicated. The arrows indicate the region in Sro7p recovered by two-hybrid and used for the in vitro binding assays. The BLAST analysis shows the smallest sum probability (in parentheses) and highest scoring region (scores <10−3 are considered potentially significant).